napari 3D filament annotator
Annotation of filaments / curvilinear structures in 3D
3D Filament Annotator is a tool for annotating filaments and other curvilinear structures in 3D. The 3D annotation is done by annotating the filament in two different projections, calculating intersection, and refining the filament position with active contours.
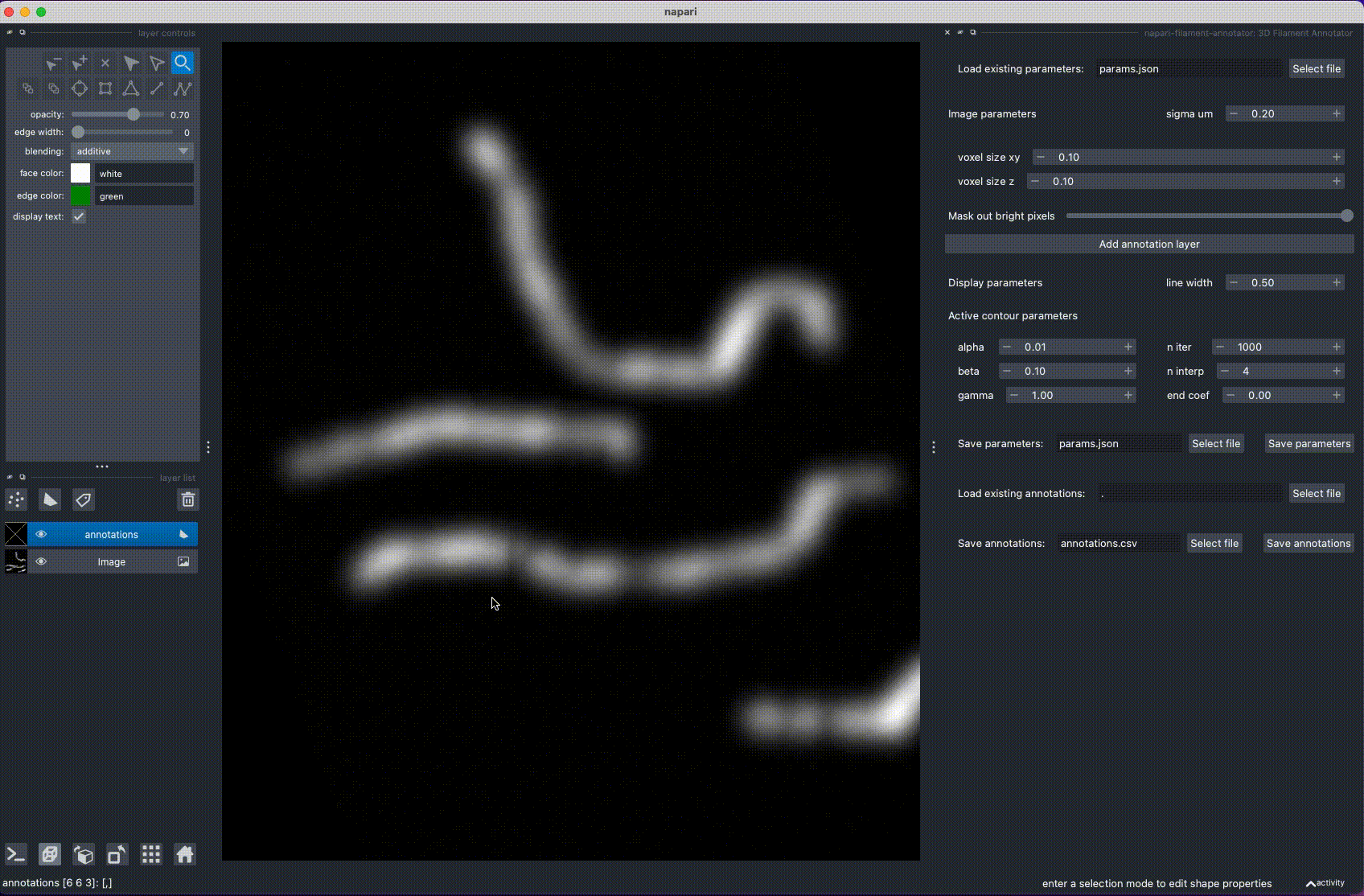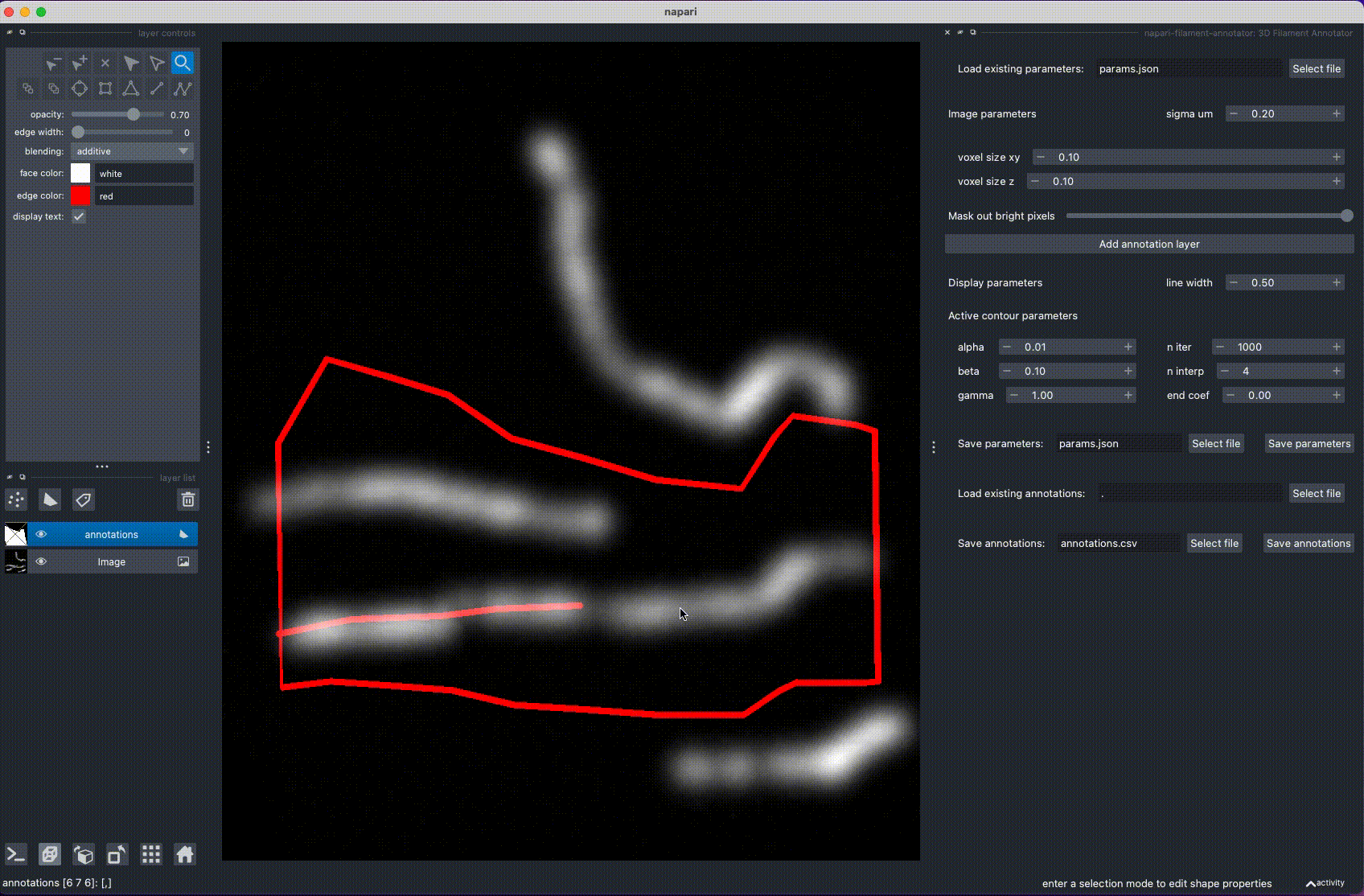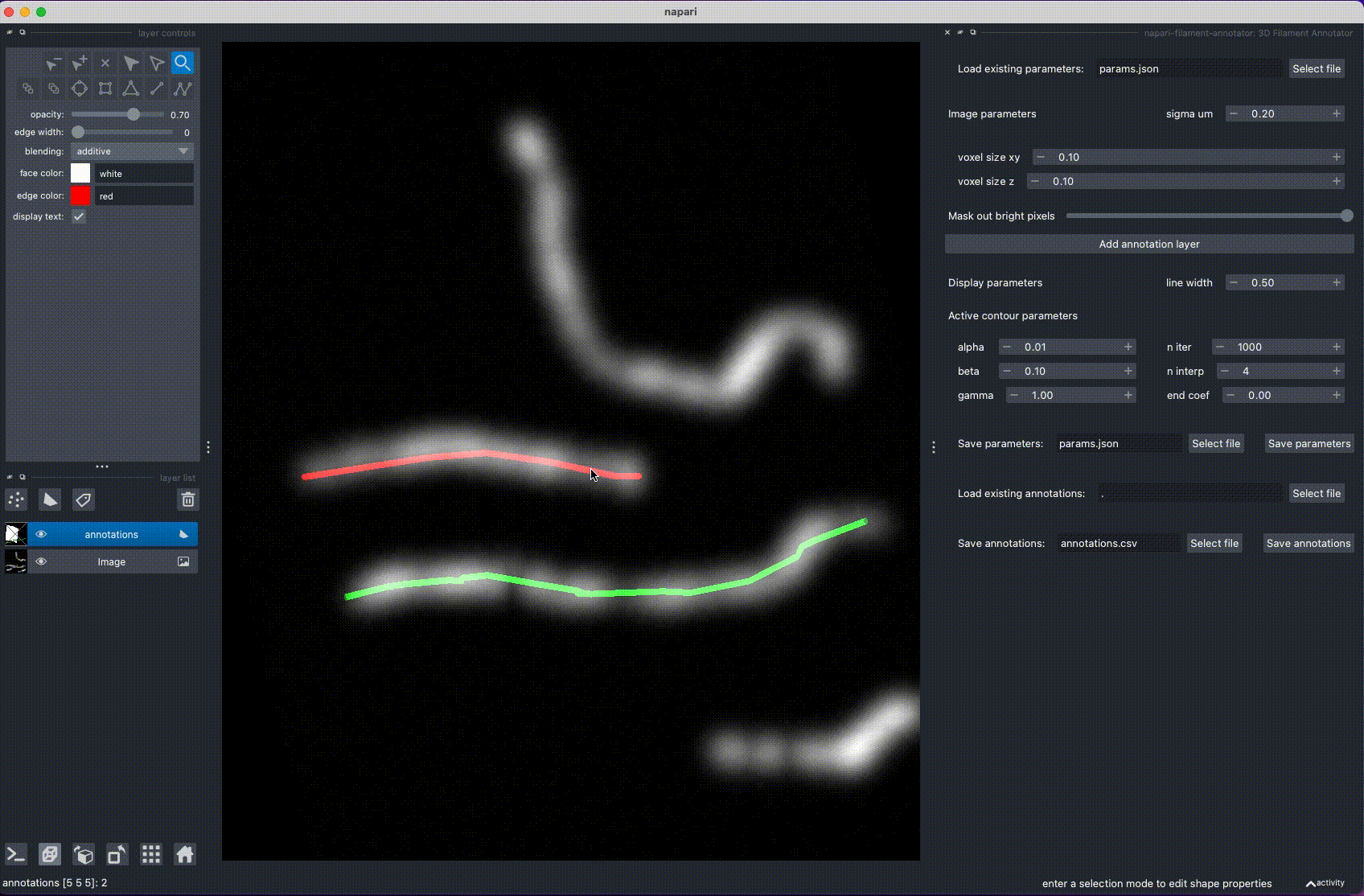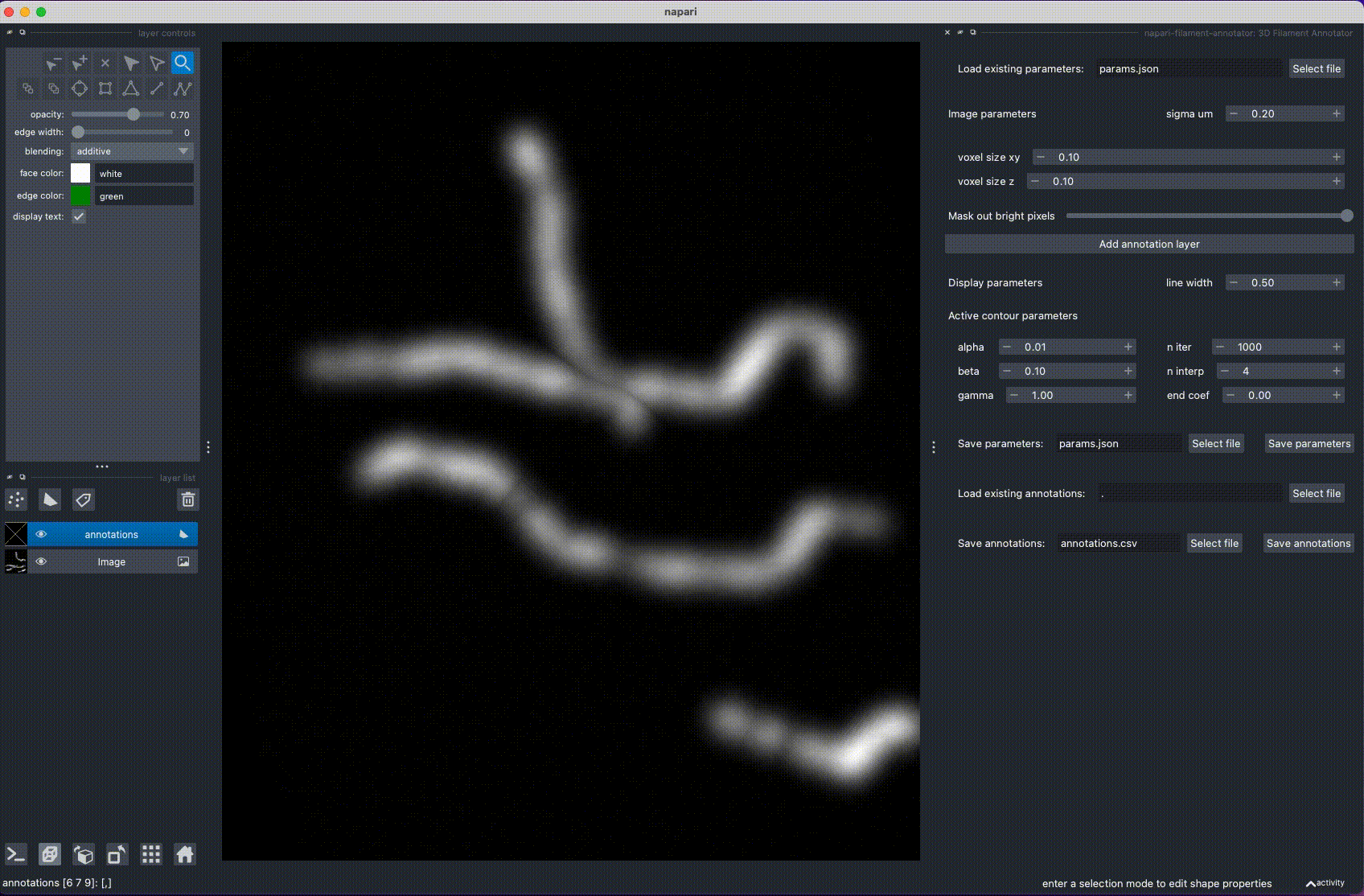
Installation
Install napari
pip install napari[all]
Install the filament annotator
pip install git+https://github.com/amedyukhina/napari-filament-annotator.git
Usage
For detailed usage instructions, please refer to the usage tutorial.
Contributing
Contributions are very welcome both with regard to plugin functionality, and tips on using it and setting parameters.
Tests can be run with tox, please ensure the coverage at least stays the same before you submit a pull request.
License
Distributed under the terms of the Apache Software License 2.0 license, "napari-filament-annotator" is free and open source software
Dependencies
Issues
If you encounter any problems, please file an issue along with a detailed description.
This napari plugin was generated with Cookiecutter using @napari's cookiecutter-napari-plugin template.
Version:
- 0.1.2
Last updated:
- 2022-10-06
First released:
- 2022-10-04
License:
- Apache
Supported data:
- Information not submitted
Plugin type:
Open extension:
Save extension:
Operating system:
- Information not submitted
Requirements:
- Geometry3D
- networkx
- numpy
- magicgui
- pandas
- qtpy
- scipy
- sklearn
- imageio (!=2.22.1)
- tox ; extra == 'testing'
- pytest ; extra == 'testing'
- pytest-cov ; extra == 'testing'
- pytest-qt ; extra == 'testing'
- napari ; extra == 'testing'
- pyqt5 ; extra == 'testing'





