napari-chatgpt | Omega
Omega: an autonomous LLM-powered agent for conversational image processing and analysis in napari. Supports OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google Gemini.
A napari plugin that leverages Large Language Models to implement Omega, a napari-aware agent capable of performing image processing and analysis tasks in a conversational manner.
This repository started as a 'week-end project' by Loic A. Royer who leads a research group at the Chan Zuckerberg Biohub. It uses LiteMind, an LLM abstraction library supporting multiple providers including OpenAI, Anthropic (Claude), and Google Gemini, as well as napari, a fast, interactive, multi-dimensional image viewer for Python, another week-end project, initially started by Loic and Juan Nunez-Iglesias.
What is Omega?
Omega is an LLM-based and tool-armed autonomous agent that demonstrates the potential for Large Language Models (LLMs) to be applied to image processing, analysis and visualization. Can LLM-based agents write image processing code and napari widgets, correct its coding mistakes, perform follow-up analysis, and control the napari viewer? The answer appears to be yes.
The publication is available here: 10.1038/s41592-024-02310-w. The preprint can be downloaded here: 10.5281/zenodo.10828225.
In this video, I ask Omega to segment an image using the SLIC algorithm. It makes a first attempt using the implementation in scikit-image but fails because of an inexistent 'multichannel' parameter. Realizing that, Omega tries again, and this time succeeds:
https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/1870994/235768559-ca8bfa84-21f5-47b6-b2bd-7fcc07cedd92.mp4
After loading a sample 3D image of cell nuclei in napari, I asked Omega to segment the nuclei using the Otsu method. My first request was vague, so it just segmented foreground versus background. I then ask to segment the foreground into distinct segments for each connected component. Omega does a rookie mistake by forgetting to 'import np'. No problem; it notices, tries again, and succeeds:
https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/1870994/235769990-a281a118-1369-47aa-834a-b491f706bd48.mp4
In this video, one of my favorites, I ask Omega to make a 'Max color projection widget.' It is not a trivial task, but it manages!
https://github.com/royerlab/napari-chatgpt/assets/1870994/bb9b35a4-d0aa-4f82-9e7c-696ef5859a2f
As LLMs improve, Omega will become even more adept at handling complex image processing and analysis tasks. Through the LiteMind library, Omega supports multiple LLM providers including OpenAI (GPT-5, GPT-4o), Anthropic (Claude Opus, Sonnet, Haiku), and Google Gemini (Gemini 3, Gemini 2.5 Pro/Flash). Many of the videos (see below and here) are highly reproducible, with a typically 90% success rate (see preprint for a reproducibility analysis).
Omega could eventually help non-experts process and analyze images, especially in the bioimage domain. It is also potentially valuable for educative purposes as it could assist in teaching image processing and analysis, making it more accessible. Although the LLMs powering Omega may not yet be on par with an expert image analyst or computer vision expert, it is just a matter of time...
Omega holds a conversation with the user and uses different tools to answer questions, download and operate on images, write widgets for napari, and more.
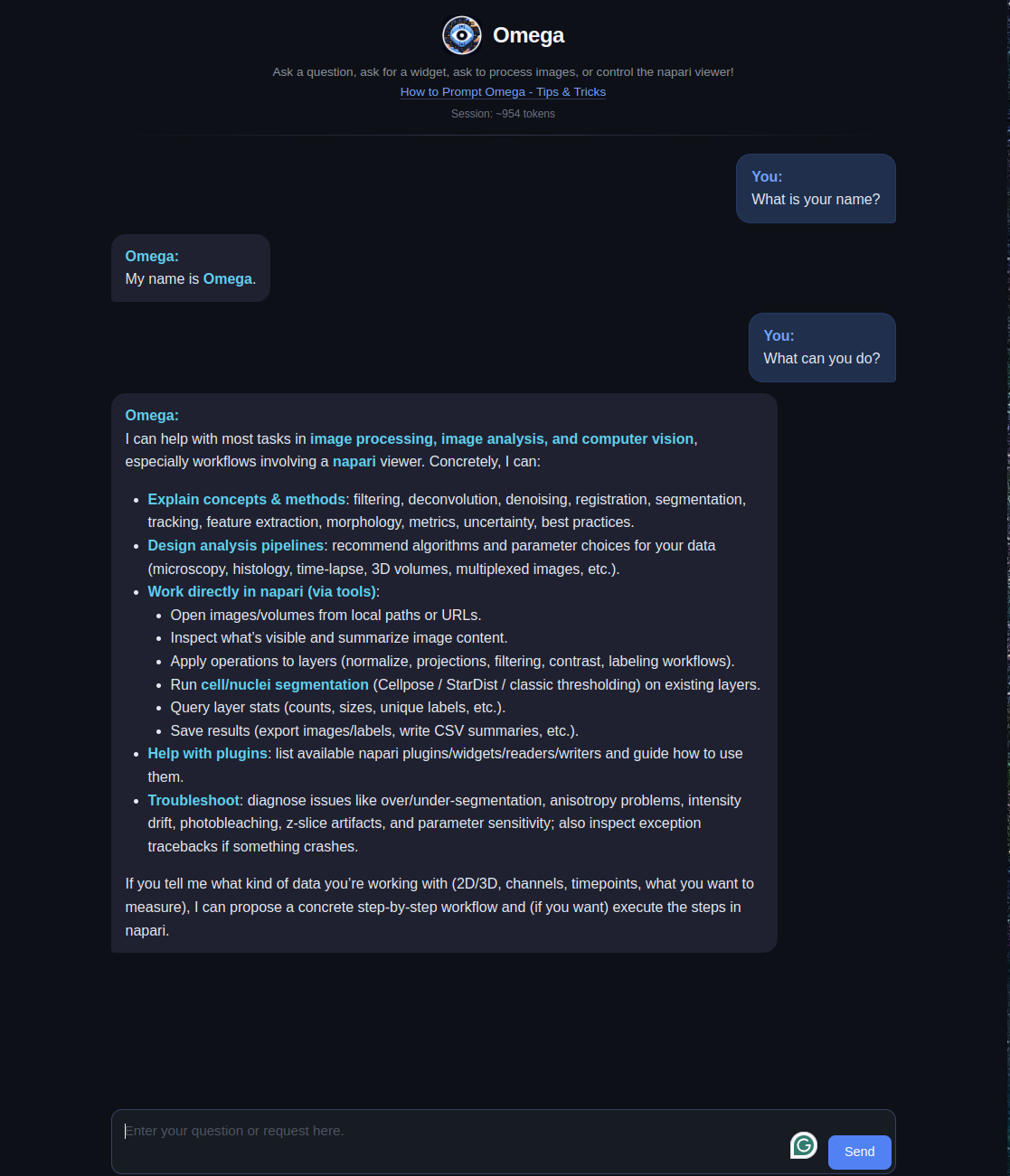
Omega's Tools
Omega comes with a comprehensive set of built-in tools:
- Viewer Control -- manipulate the napari viewer (camera, layers, rendering)
- Widget Creation -- generate custom napari widgets from natural language
- Image Segmentation -- classic (Otsu/watershed), Cellpose, and StarDist segmentation
- Image Denoising -- AI-powered denoising via Aydin
- Viewer Vision -- screenshot-based visual analysis of the viewer contents
- napari Plugin Integration -- discover and use any installed napari plugin (readers, writers, widgets)
- File Download -- download files from URLs for subsequent processing
- Python Functions Info -- query signatures and docstrings of any Python function
- Package Info -- search installed Python packages
- Pip Install -- install Python packages (with user permission)
- Exception Catcher -- catch and report uncaught exceptions for debugging
- Web Search -- search the web, Wikipedia, and find images
- Python REPL -- execute arbitrary Python code
Here is an example of Omega creating a custom image registration widget in napari:
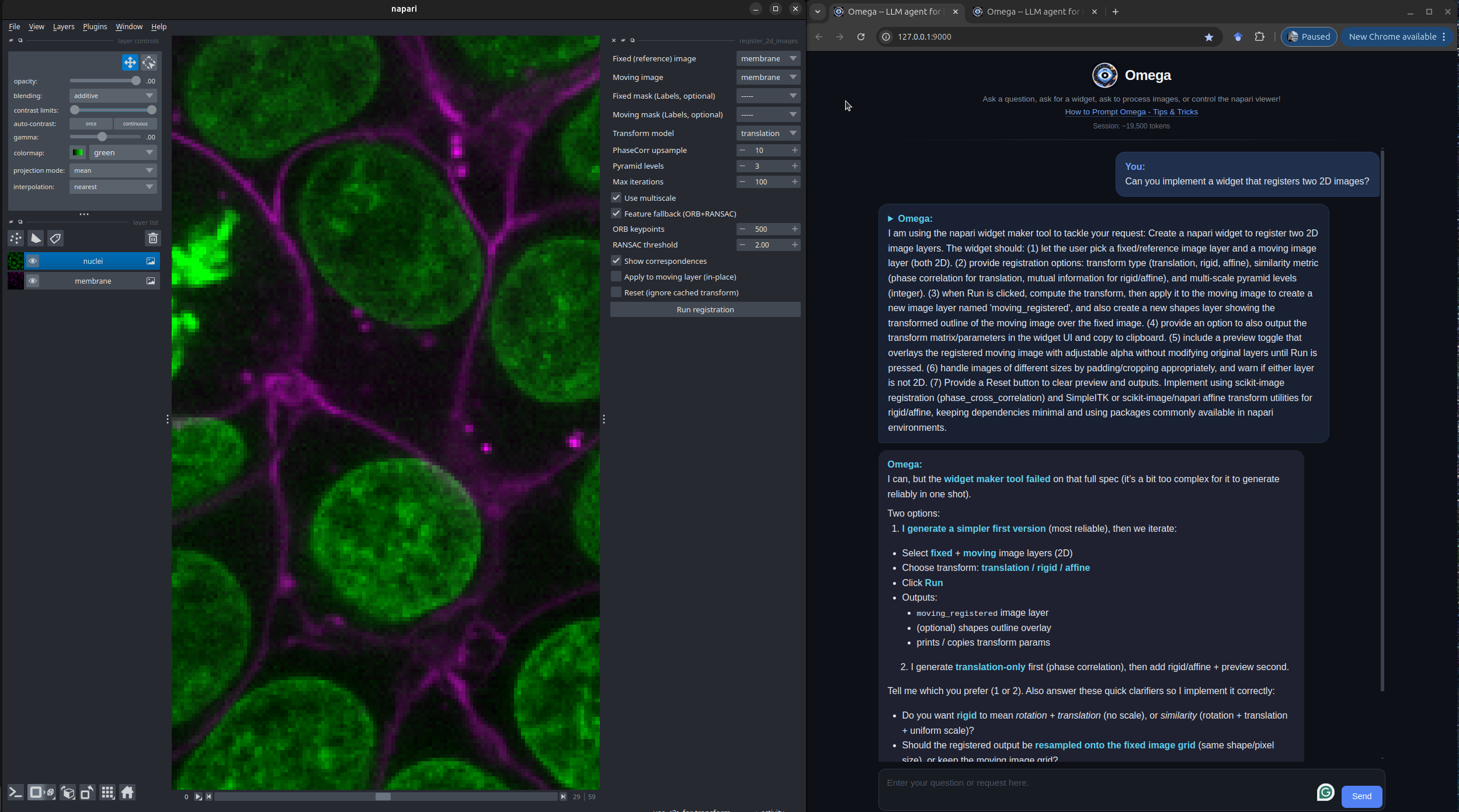
Omega's Built-in AI-Augmented Code Editor
The Omega AI-Augmented Code Editor is a new feature within Omega, designed to enhance the Omega's user experience. This editor is not just a text editor; it's a powerful interface that interacts with the Omega dialogue agent to generate, optimize, and manage code for advanced image analysis tasks.
Key Features
- Code Highlighting and Completion: For ease of reading and writing, the code editor comes with built-in syntax highlighting and intelligent code completion features.
- LLM-Augmented Tools: The editor is equipped with AI tools that assist in commenting, cleaning up, fixing, modifying, and performing safety checks on the code.
- Persistent Code Snippets: Users can save and manage snippets of code, preserving their work across multiple Napari sessions.
- Network Code Sharing (Code-Drop): Facilitates the sharing of code snippets across the local network, empowering collaborative work and knowledge sharing.
Usage Scenarios
- Widget Creation: Expert users can create widgets using the Omega dialogue agent and retain them for future use.
- Collaboration: Share custom widgets with colleagues or the community, even if they don't have access to an API key.
- Learning: New users can learn from the AI-augmented suggestions, improving their coding skills in Python and image analysis workflows.
You can find more information in the corresponding wiki page.
Omega's Installation instructions:
Assuming you have a Python environment with a working napari installation, you can simply:
pip install napari-chatgpt
Or install the plugin from napari's plugin installer.
For detailed instructions and variations, check this page of our wiki.
Key Dependencies
- LiteMind -- LLM abstraction (OpenAI, Anthropic, Gemini)
- napari >= 0.5
- FastAPI/Uvicorn -- WebSocket chat server
- scikit-image -- image processing
- beautifulsoup4 -- web scraping
- requests -- HTTP downloads
- Python 3.10+ supported
Requirements:
You need an API key from at least one supported LLM provider:
- OpenAI - Get your key at platform.openai.com
- Anthropic (Claude) - Get your key at console.anthropic.com
- Google Gemini - Get your key at aistudio.google.com
- GitHub Models - Auto-detected if
GITHUB_TOKENis set - Custom endpoints - Any OpenAI-compatible API (local LLMs, Azure, etc.)
Check here for details on API key setup. Omega will automatically detect which providers you have configured.
GitHub Models (free)
If you have a GitHub personal access token, Omega can use
models from the GitHub Models marketplace (GPT-4o, Llama,
Phi, Mistral, and more) for free with rate limits. Just set the GITHUB_TOKEN environment variable:
export GITHUB_TOKEN="ghp_your_token_here"
Omega auto-detects this token on startup and registers all available GitHub Models.
Custom OpenAI-compatible endpoints
You can connect Omega to any OpenAI-compatible API (Azure OpenAI, local LLMs via Ollama/vLLM, or
third-party providers) by adding entries to ~/.omega/config.yaml:
custom_endpoints:
- name: "Azure GPT-4"
base_url: "https://my-resource.openai.azure.com/openai/deployments/gpt-4/v1"
api_key_env: "AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY"
- name: "Local Ollama"
base_url: "http://localhost:11434/v1"
api_key_env: "OLLAMA_API_KEY"
Each endpoint requires a base_url and an api_key_env (the name of the environment variable
holding the API key). Models discovered from these endpoints appear in the model dropdown alongside
built-in providers.
Extending Omega with custom tools
External packages can register new tools for Omega via Python entry points. Create a class that
subclasses BaseOmegaTool and declare it in your pyproject.toml:
[project.entry-points."napari_chatgpt.tools"]
my_tool = "my_package.tools:MyCustomTool"
Omega discovers and loads these tools automatically on startup. See the Extensibility wiki page for full details and examples.
Usage:
Check this page of our wiki for details on how to start Omega.
Tips, Tricks, and Example prompts:
Check our guide on how to prompt Omega and some examples here.
Video Demos:
You can check the original release videos here. You can also find the latest preprint videos on Vimeo.
How does Omega work?
The publication is available here: 10.1038/s41592-024-02310-w. Check our preprint here: 10.5281/zenodo.10828225.
and our wiki page on Omega's design and architecture.
Cost:
LLM API costs vary by provider and model. For reference:
- OpenAI pricing: openai.com/pricing
- Anthropic pricing: anthropic.com/pricing
- Google Gemini pricing: ai.google.dev/pricing
Most providers allow you to set spending limits to control costs.
Disclaimer:
Do not use this software lightly; it will download libraries of its own volition
and write any code it deems necessary; it might do what you ask, even
if it is a very bad idea. Also, beware that it might misunderstand what you ask and
then do something bad in ways that elude you. For example, it is unwise to use Omega to delete
'some' files from your system; it might end up deleting more than that if you are unclear in
your request.
Omega is generally safe as long as you do not make dangerous requests. To be 100% safe, and
if your experiments with Omega could be potentially problematic, I recommend using this
software from within a sandboxed virtual machine.
API keys are only as safe as the overall machine is, see the section below on API key hygiene.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED “AS IS”, WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
API key hygiene:
Best Practices for Managing Your API Keys:
- Host Computer Hygiene: Ensure that the machine you're installing napari-chatgpt/Omega on is secure, free of malware and viruses, and otherwise not compromised. Make sure to install antivirus software on Windows.
- Security: Treat your API key like a password. Do not share it with others or expose it in public repositories or forums.
- Cost Control: Set spending limits on your LLM provider account: OpenAI | Anthropic | Google Gemini
- Regenerate Keys: If you believe your API key has been compromised, revoke and regenerate it from your provider's console immediately: OpenAI | Anthropic | Google Gemini
- Key Storage: Omega has a built-in 'API Key Vault' that encrypts keys using a password, this is the preferred approach. You can also store the key in an environment variable, but that is not encrypted and could compromise the key.
Contributing
Contributions are extremely welcome. The project uses a Makefile for development:
make setup # Install with dev dependencies + pre-commit hooks
make test # Run all tests
make test-cov # Run tests with coverage
make format # Format code with black and isort
make check # Run all code checks
Please ensure the coverage stays the same before you submit a pull request.
License
Distributed under the terms of the BSD-3 license, "napari-chatgpt" is free and open-source software
Issues
If you encounter any problems, please file an issue along with a detailed description.
Version:
- 2026.2.9
Last updated:
- 2026-02-10
First released:
- 2023-05-03
License:
- BSD-3-Clause
Supported data:
- Information not submitted
Plugin type:
Open extension:
Save extension:
Operating system:
- Information not submitted
Requirements:
- arbol
- beautifulsoup4>=4.12
- black>=23.0
- cryptography>=43.0
- duckduckgo-search>=7.0.0
- fastapi>=0.109
- httpx>=0.24
- imageio[ffmpeg,pyav]>=2.31
- jedi>=0.18
- litemind>=2026.2.1
- lxml-html-clean
- lxml>=4.9
- magicgui>=0.7
- matplotlib>=3.7
- napari>=0.5
- nbformat>=5.7
- numba>=0.60
- numpy>=1.26
- ome-zarr>=0.8
- qtawesome>=1.0
- qtpy>=2.0
- requests>=2.28
- scikit-image>=0.21
- tabulate>=0.9
- uvicorn>=0.20
- websockets>=11.0
- xarray<2025,>=2024.1.0
- cellpose; extra == 'testing'
- napari; extra == 'testing'
- npe2; extra == 'testing'
- nvidia-cuda-nvcc-cu12; extra == 'testing'
- pyqt5; extra == 'testing'
- pytest; extra == 'testing'
- pytest-cov; extra == 'testing'
- pytest-mock; extra == 'testing'
- pytest-qt; extra == 'testing'
- pytest-xvfb; extra == 'testing'
- stardist; extra == 'testing'
- tensorflow; extra == 'testing'
- tox; extra == 'testing'








