DoMB
napari plugin for analyzing the redistribution of fluorescence-labeled proteins
domb-napari
napari Toolkit of Department of Molecular Biophysics
Bogomoletz Institute of Physiology of NAS of Ukraine, Kyiv, Ukraine
This plugin offers widgets specifically designed to analyze the redistribution of fluorescence-labeled proteins in widefield epifluorescence time-lapse acquisitions. It is particularly useful for studying various phenomena, including:
- Calcium-dependent translocation of neuronal calcium sensors.
- Synaptic receptor traffic.
- Membrane protein tracking.
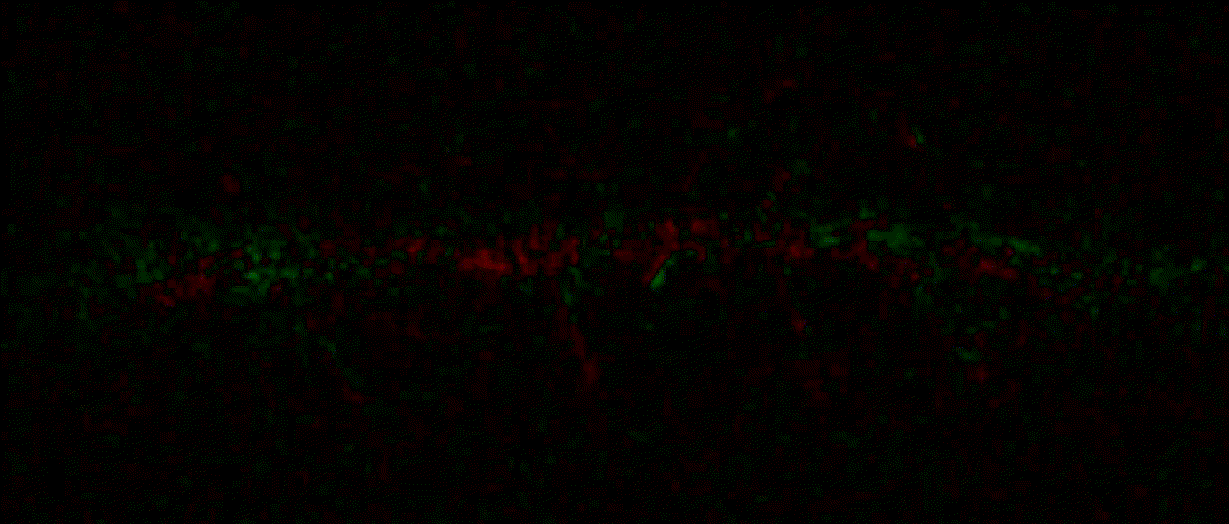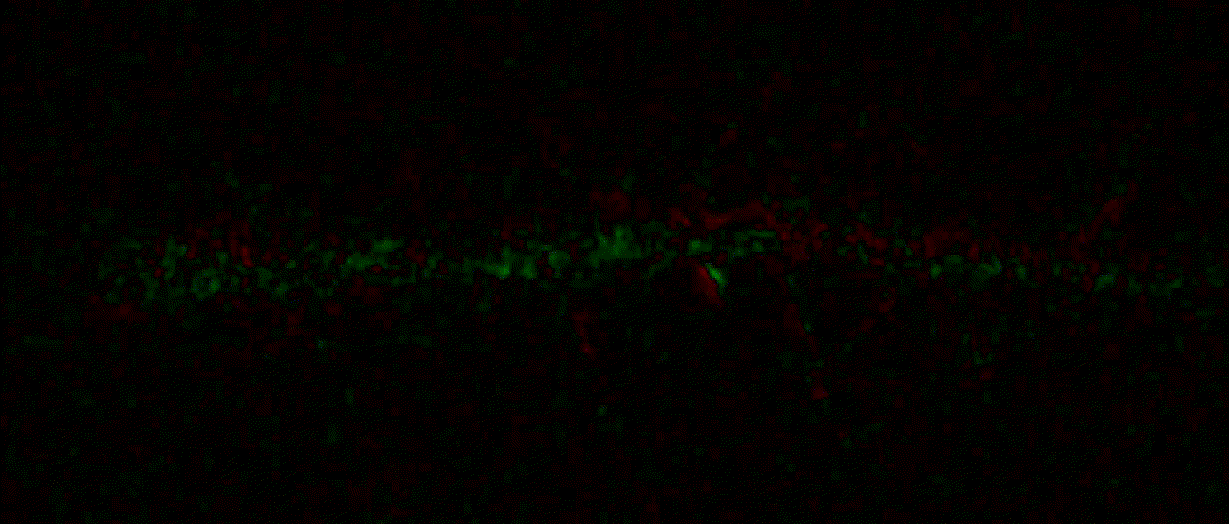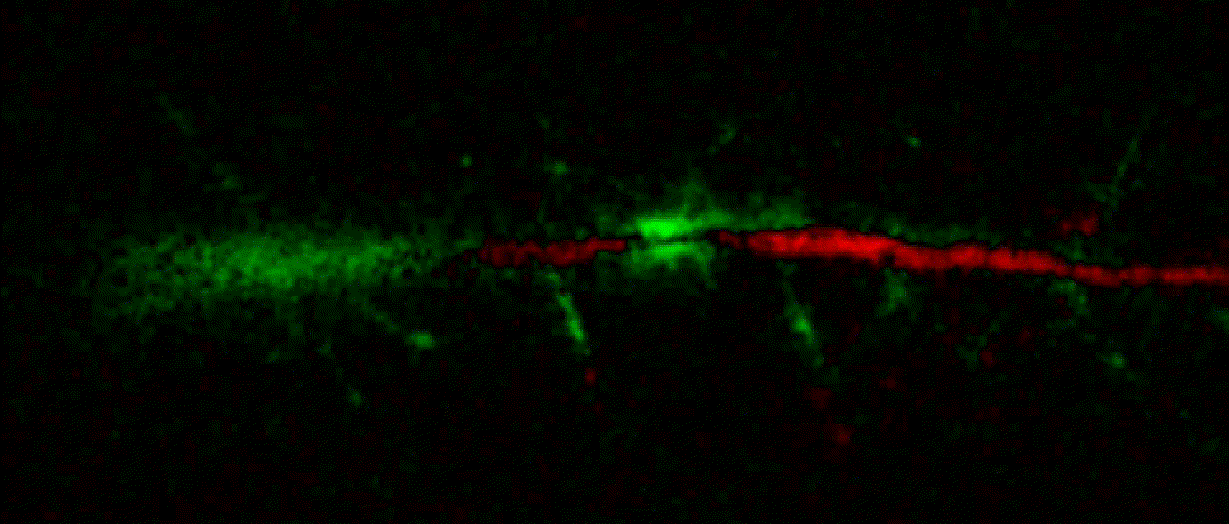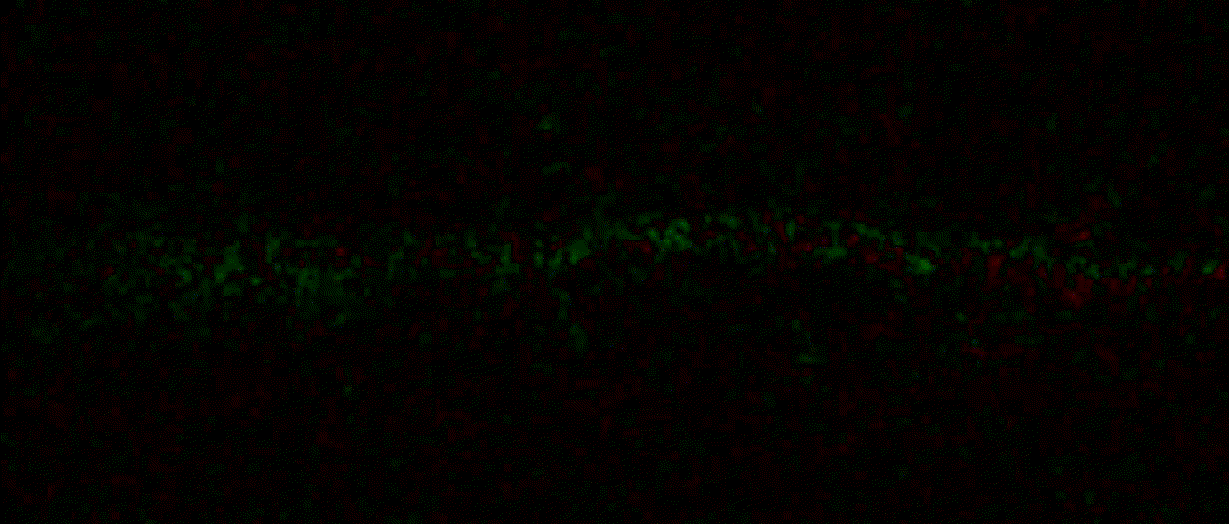 Hippocalcin (neuronal calcium sensor) redistributes in dendritic branches upon NMDA application
Hippocalcin (neuronal calcium sensor) redistributes in dendritic branches upon NMDA application
Plugin Menus
The plugin widgets are distributed across the following napari Layers menus:
- Visualize
Labels Profilessubmenu: ROIs profiles, Multiple img stat profiles, Multiple labels stat profiles
- Data
Preprocessingsubmenu: Multichannel stack preprocessing, Dual-view stack registration- Save Data Frame
- Measure
- Red-green series
- ΔF series
FRETsubmenu: E-FRET estimation, E-FRET G-factor estimation, E-FRET crosstalk estimation
- Segment
- Dot-patterns masking
- Up masking
- Intensity masking
Plugin Structure
graph TD
subgraph Preprocessing [Preprocessing]
MP[Multichannel Image Preprocessing]
R[Multichannel Image Registration]
R --> MP
end
subgraph Analysis [Analysis]
DF[ΔF Series]
RG[Red-green Series]
end
MP ==> Analysis
subgraph FRET [FRET]
subgraph Calibration [Calibration]
FC[Cross-talk Estimation]
FG[G-factor Estimation]
end
FR[FRET Estimation]
end
MP ==> FRET
FR ---> Analysis
FR ---> Segmentation
subgraph Segmentation [Segmentation]
UP[Up Masking]
DOWN[Masking]
DOT[Dot-pattern Masking]
end
%% MP ==> Segmentation
Analysis ==> Segmentation
subgraph Vis [Visualization & Data Saving]
subgraph Stat [Aggregated Plots]
MIP[Multiple Images Profiles]
MMP[Multiple Masks Profiles]
end
RP[ROIs Profiles]
DAT[Data Frame Saving]
end
Segmentation ==> Vis
FRET ==> Vis
E-FRET Module Structure
flowchart TD
%% INPUT DATA
%% Input[/Input Images:<br/> I<sub>DD</sub>, I<sub>DA</sub>, I<sub>AA</sub>/]:::data
Input@{shape: manual-input, label: "Input Images:<br/> I<sub>DD</sub>, I<sub>DA</sub>, I<sub>AA</sub>"}
%% Mask[/ROIs Mask/]:::data
Mask@{shape: manual-input, label: "ROIs Mask"}
%% CALIBRATION
subgraph Calibration [Coefficients Estimation]
%% direction TB
CT[_CrossTalkEstimation_ Class]:::algo
GF[_GFactorEstimation_ Class]:::algo
Coeffs(Cross-talk coefs. __a__ & __d__):::result
GF_Val(__G__ factor):::result
Input -->|Samples with A or D only| CT
Mask --> CT
CT -->|Linear regression| Coeffs
Input -->|Samples with AD tandem| GF
Mask & Coeffs --> GF
GF -->|Zal / Chen method| GF_Val
end
%% ANA
subgraph Analysis [FRET Estimation]
%% direction TB
Main[_CubesFRET_ Class]:::algo
Numba[[JIT compiled Numba functions]]:::algo
Output(Pixel-wise FRET estimation:<br/> F<sub>c</sub>, E<sub>D</sub>, E<sub>A</sub>, E<sub>corr</sub>):::result
Input ==> Main
Coeffs & GF_Val ==> Main
Main ==> Output
Main <-...->|Pixel-wise calc| Numba
end
Preprocessing
Dual-view Stack Registration
Registration of four-channel image stacks, including two excitation wavelengths and two emission pathbands, acquired with a dual-view beam splitter. This setup detects different spectral pathbands using distinct sides of the camera matrix.
offset img- input for a four-channel time-lapse image stack.input crop- number of pixels to remove from each side of input frames to eliminate beam-splitter alignment artifacts.output crop- number of pixels to remove from each side of output frames to eliminate registration edge artifacts.align method- choice between:internal- automated registration based on the input stack.load matrix- applies a pre-calculated affine transformation matrix from a.txtfile.
manual channels- enables manual selection of Reference and Offset channels for registration.ref_off_ch- defines which spectral channels to use for offset estimation.save matrix- exports the calculated affine transformation matrix to a.txtfile at the specifiedsaving path.
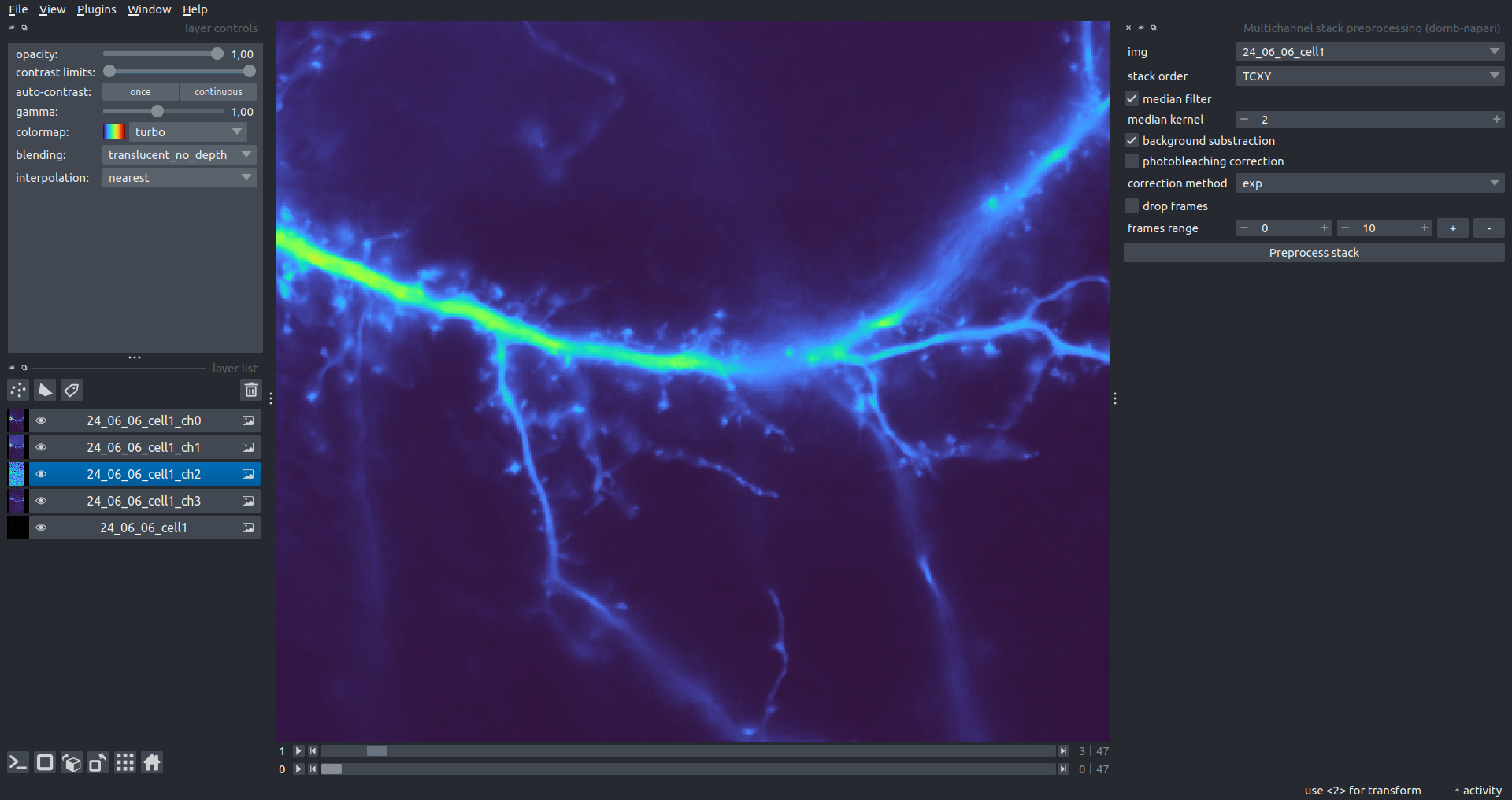
Multichannel Stack Preprocessing
stack order- specifies the axis order of the input data: T (time), C (channel), X, and Y.median filter- applies frame-by-frame smoothing with a kernel size specified inmedian kernel.background subtraction- compensates for background fluorescence. The background is estimated as the 1.0 percentile of frame intensity.photobleaching correction- fits the total intensity decay using exponential (exp) or bi-exponential (bi_exp) models.correction mask- an optional Labels layer to define the area for bleaching estimation (e.g., cell body).
drop frames- enables cropping the time sequence based on theframes range(start/stop indices).frames crop- crops the image borders by a specified number of pixels.
Detection of Fluorescence Redistribution
A set of widgets designed for preprocessing multispectral image stacks and detecting redistributions in fluorescence intensity. These widgets specifically analyze differential "red-green" image series to identify changes in fluorescence intensity.
Inspired by Dovgan et al., 2010 and Osypenko et al., 2019.
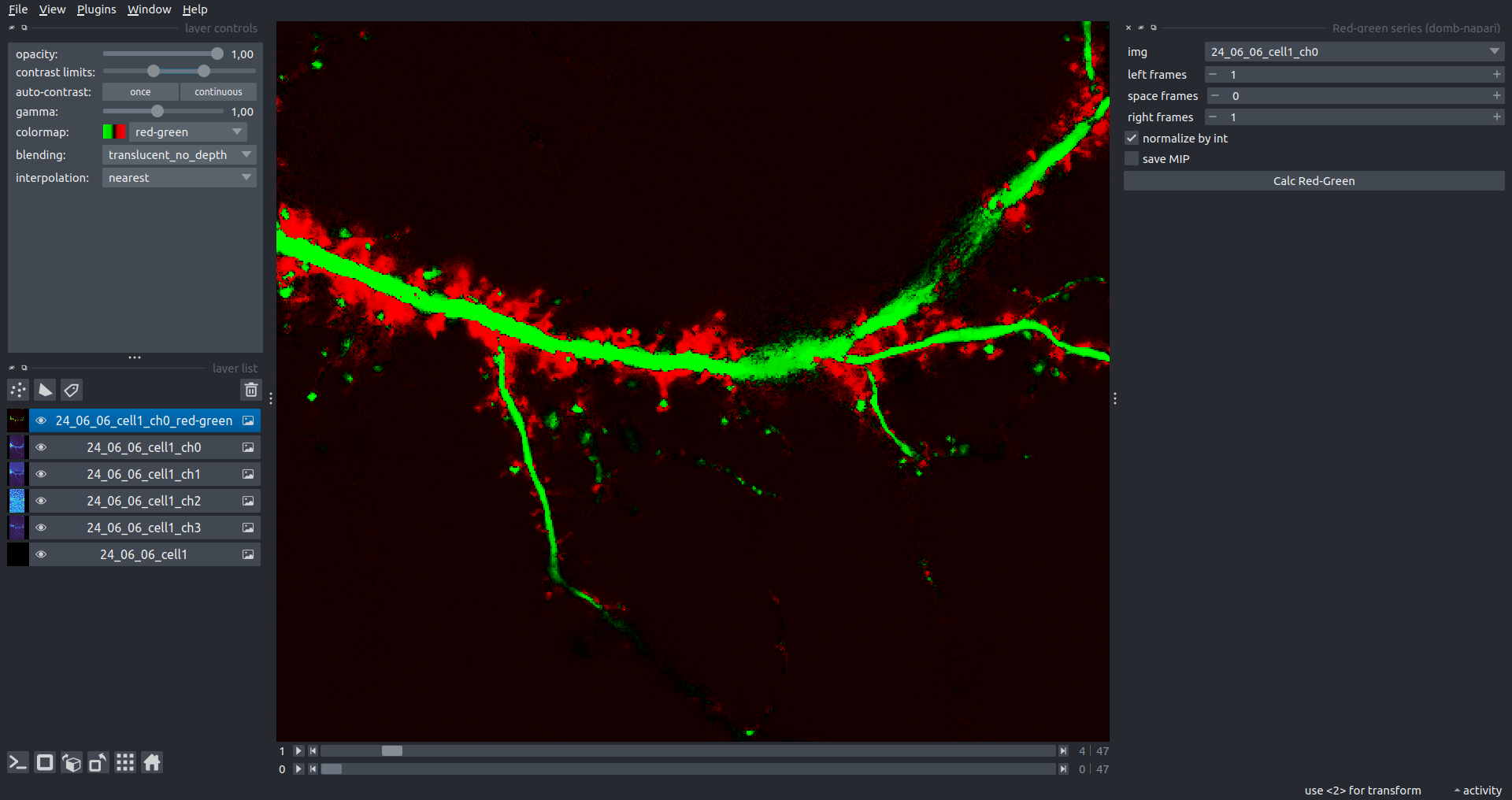
Red-Green Series
Primary method for detecting fluorescence-labeled targets redistribution. This widget returns a series of differential images, each representing the intensity difference between the current frame and the previous one, output image labeled with the _red-green suffix.
Parameters:
left frames- specifies the number of previous frames used for pixel-wise averaging.space frames- determines the number of frames between the last left frame and the first right frame.right frames- specifies the number of subsequent frames used for pixel-wise averaging.
normalize by int function normalizes the differential images relative to the absolute intensity of the input image stack, which helps to reduce background noise amplitude.
If save MIP is selected, the maximal intensity projection (MIP) of the differential image stack will be saved with the _red-green-MIP suffix.
ΔF Series
Calculates relative intensity changes for time-lapse images.
Parameters:
values mode- detection mode:ΔF- absolute intensity changes ($F(t) - F_{0}$).ΔF/F0- relative intensity changes ($(F(t) - F_{0}) / F_{0}$).
F0 win- window size (number of frames) for baseline intensity ($F_{0}$) estimation.
Masking
Dots Pattern Masking
Creates labels for bright dot elements on an image, such as pre- and postsynaptic fluorescence markers (e.g., Bassoon/Synaptobrevin for presynapses, PSD-95/Homer for postsynapses, etc.). It returns a labels layer with the _dots-labels suffix.
The widget detects the location on the MIP (Maximum Intensity Projection) of the input time series image and applies simple round masks to each detected dot. Watershed segmentation is then used to prevent the merging of overlapping masks.
Parameters:
background level- Background level for filtering out low-intensity elements. This is specified as a percentile of the MIP intensity.detection level- Minimum intensity of dots, specified as a percentile of the MIP's maximum intensity.mask diameter- Diameter in pixels for the round mask of each individual dot.minimal distance- Minimum distance in pixels between the centers of individual round masks.
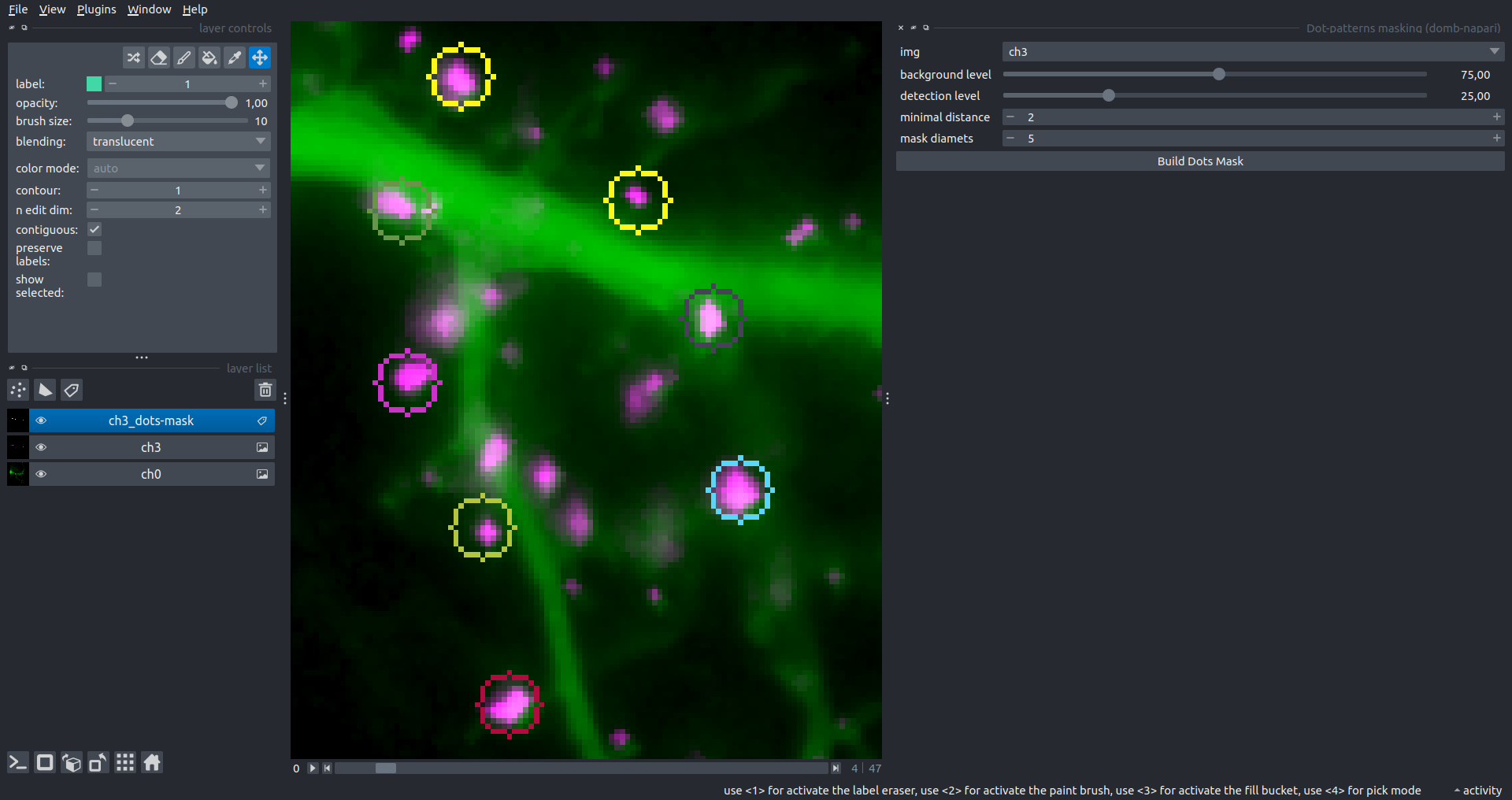 Hippocalcin (green) and PSD95 (magents) in dendritic branches
Hippocalcin (green) and PSD95 (magents) in dendritic branches
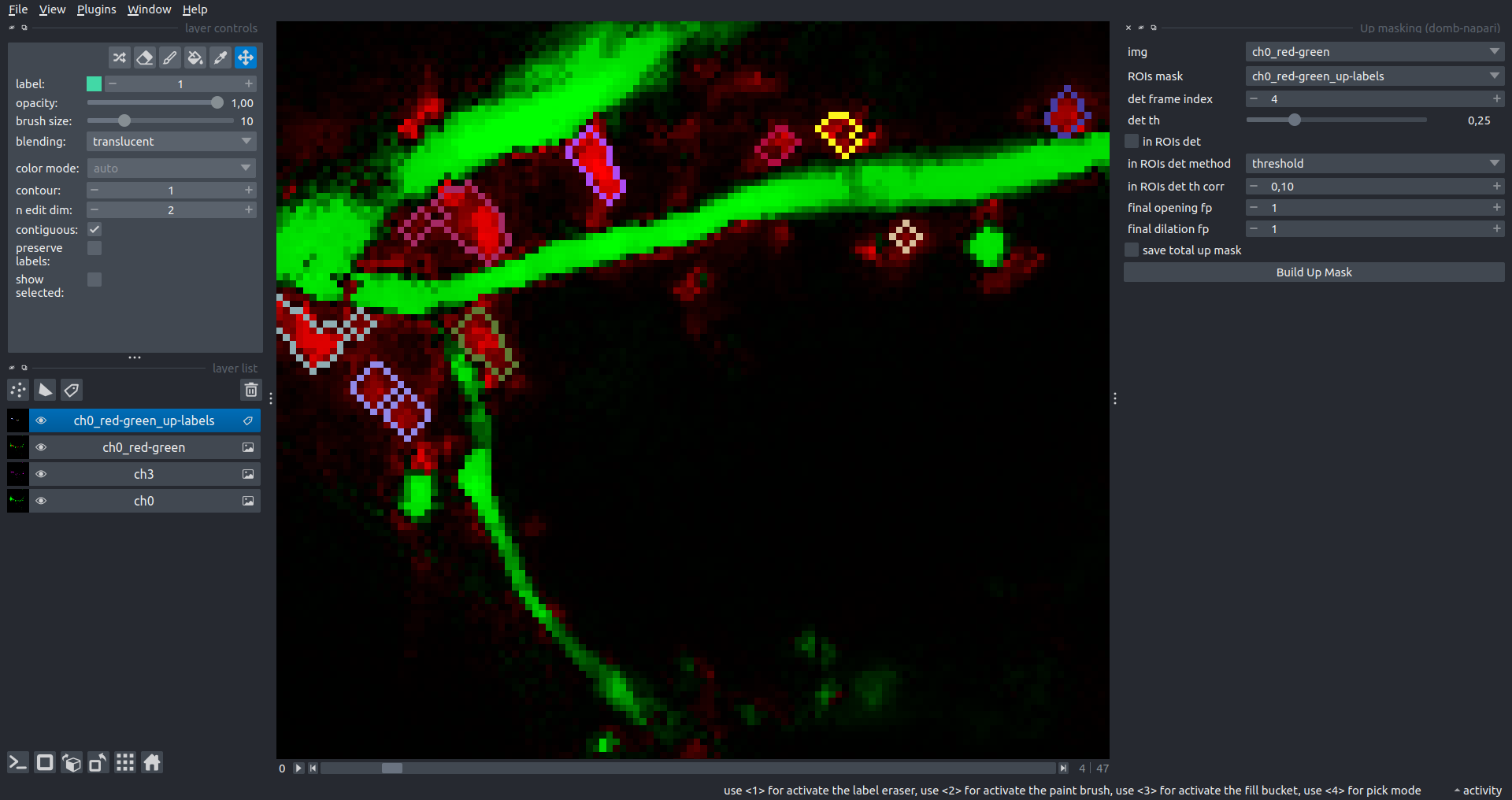
Up Masking
Generates labels for regions with high intensity based on raw or -red-green images. Returns a labels layer with the _up-labels suffix.
The widget provides two detection modes:
- Global masking with a fixed threshold for the entire image.
- In-ROIs masking with a loop over individual ROIs in the input
ROIs maskwith separate detections.
Parameters:
det frame index- index of the frame from the input image used for label detection.det th- threshold value for detecting bright sites, where the intensity on the selected frame is normalized in the range of -1 to 0.in ROIs det- option for activating in-ROIs masking.in ROIs det method- method for in-ROIs masking; otsu provides simple Otsu thresholding, while the threshold method is identical to global detection on normalized detection frame.in_ROIs_det_th_corr- scaling factor for the det th threshold value for in-ROIs masking.final opening fp- footprint size in pixels for mask filtering using morphological opening (disabled if set to 0).final dilation fp- footprint size in pixels for mask morphological dilation (disabled if set to 0).save total up mask- if selected, a total up mask (containing all ROIs) will be created with the _up-mask suffix.
 Global up labels
Global up labels
The In-ROIs masking option can be particularly useful for co-localization detection. By applying a broad reference mask to several target images, you can create more precise labels for ROIs in specified cell compartments. The following examples demonstrate the detection of mutual locations for static PSD-95 enriched sites (postsynaptic membranes) and HPCA translocation sites only in the vicinity of synapses, using _dots-labels for PSD95-mRFP images.
[!IMPORTANT] In the In-ROIs masking mode, labels of detected sites correspond to the matching labels from the input ROIs mask.
| In-ROIs masking (reference) | 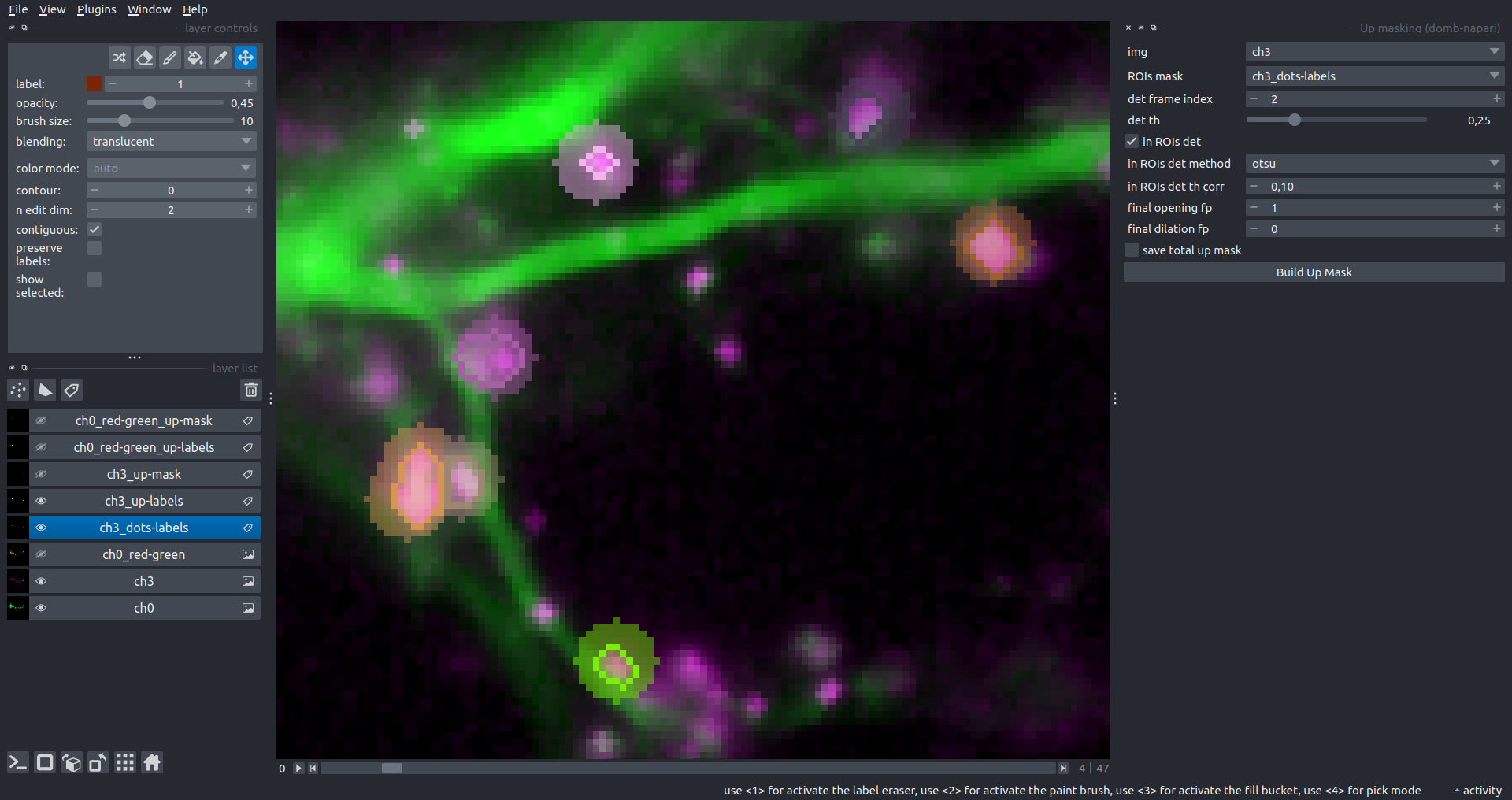 |
|---|---|
| In-ROIs masking (translocation) | 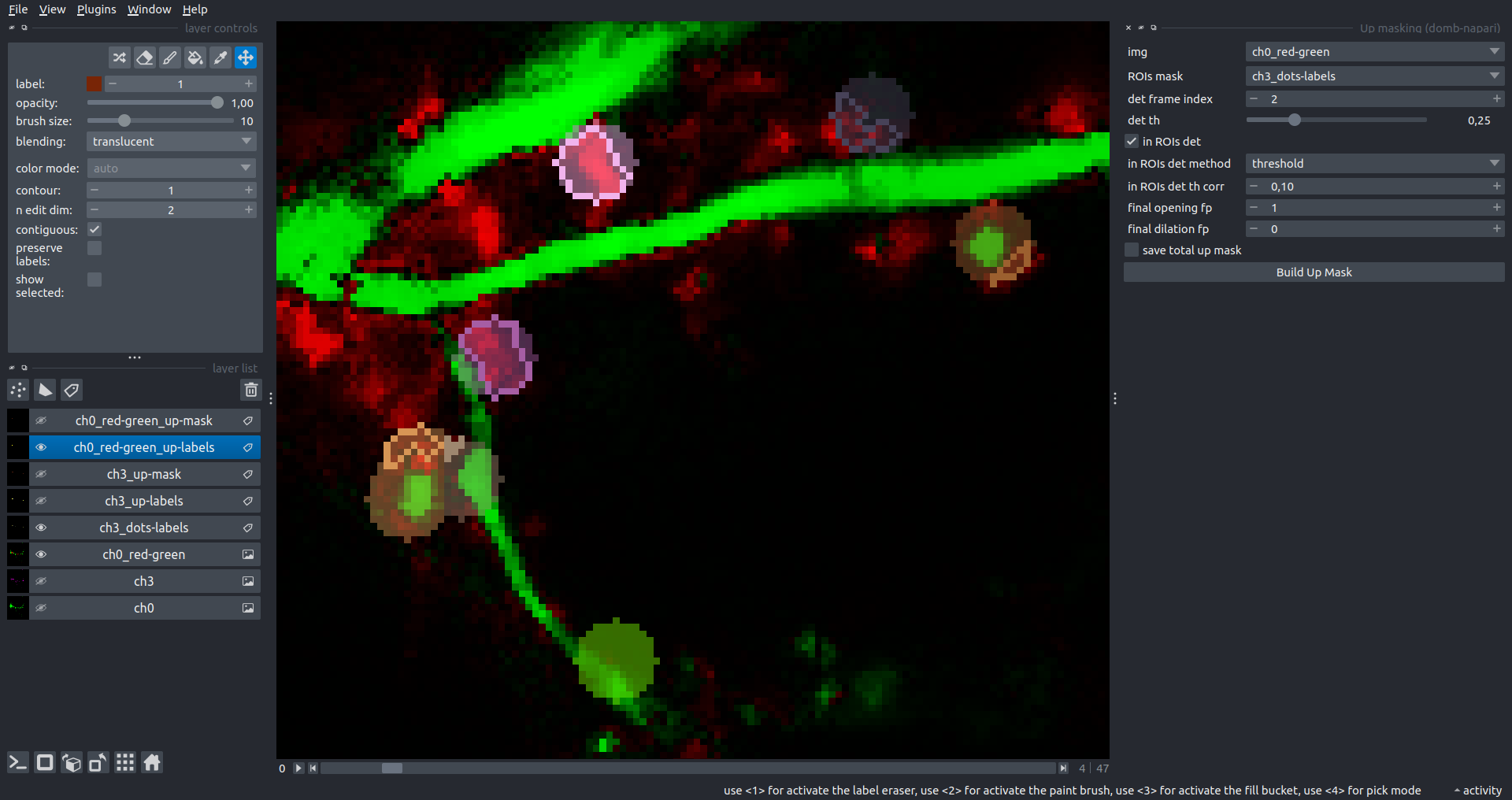 |
| Masks overlay | 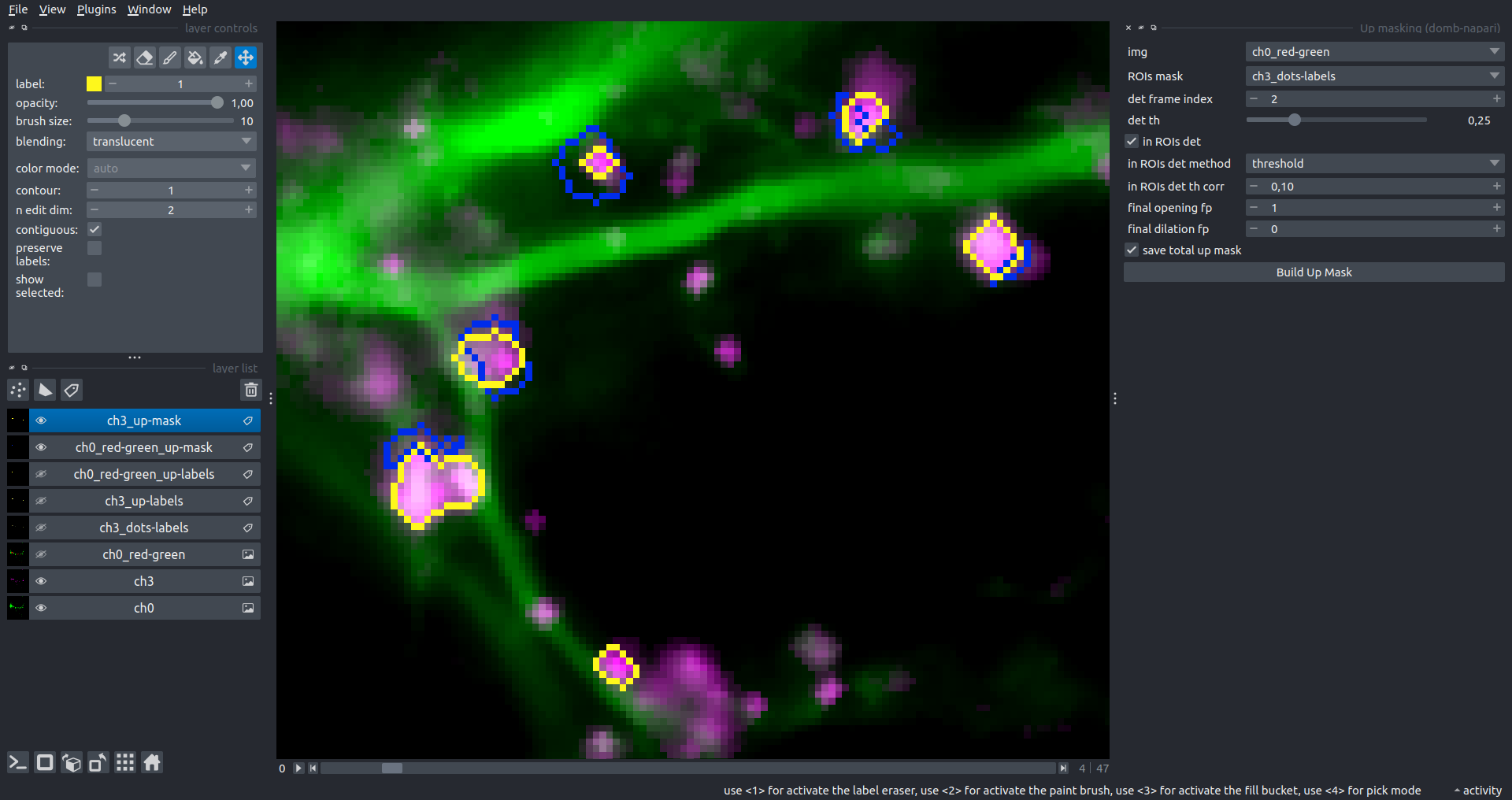 |
Intensity Masking
Extension of the Up Masking widget. Detects regions with either significantly increasing (up) or decreasing (down) intensity in -red-green differential images.
Parameters:
masking mode- defines whether to detect local intensity gains or losses.up threshold- sensitivity for detecting intensity increases (normalized to maximum intensity).down threshold- sensitivity for detecting intensity decreases.opening footprint- disk radius for morphological opening to filter out noise.
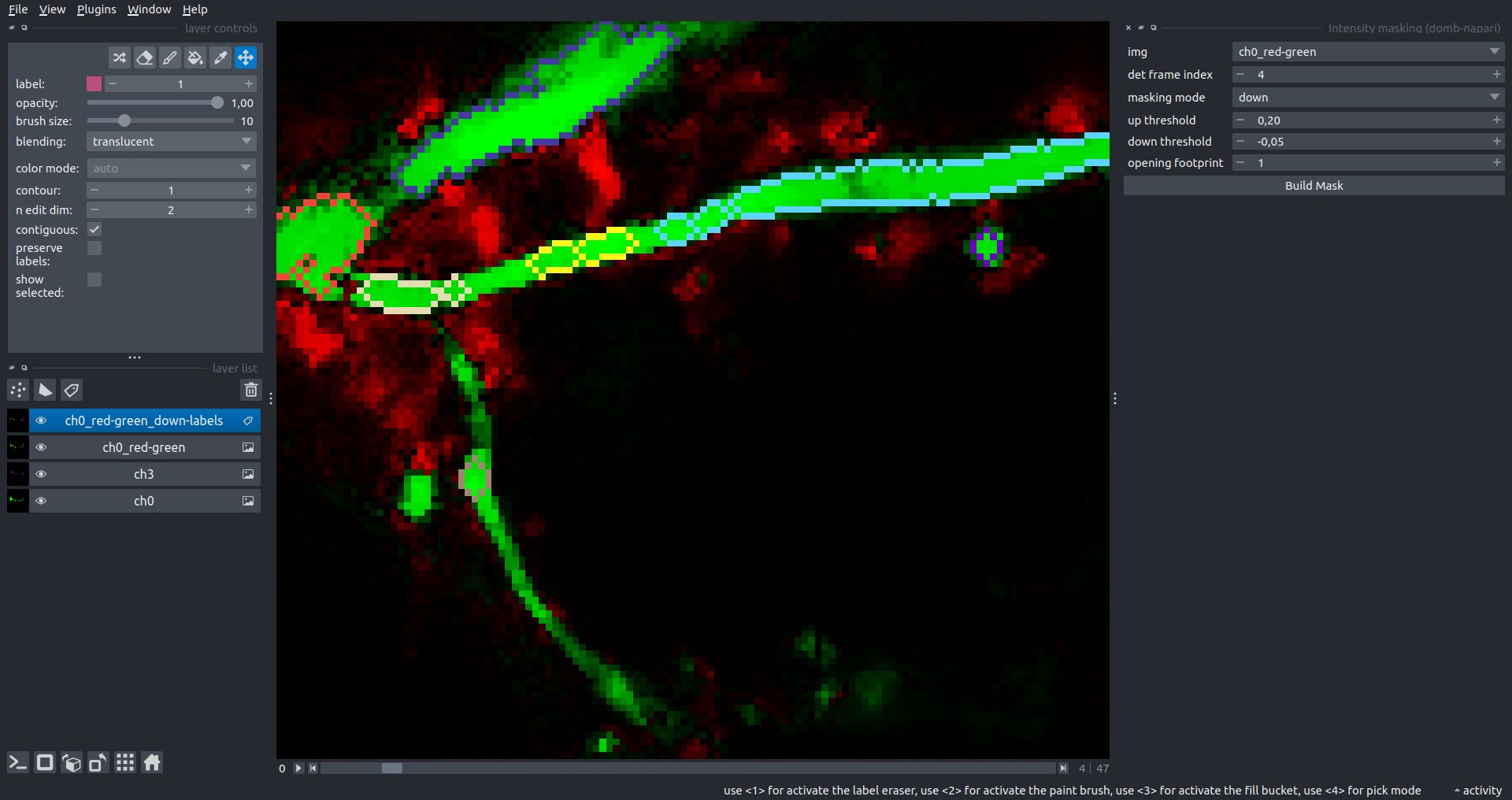
3-cube E-FRET Approach
Widgets for detection and analysis of Förster resonance energy transfer on multispectral image stacks.
Based on notation and approaches from Zal and Gascoigne, 2004, Chen et al., 2006 and Kamino et al., 2023.
E-FRET Cross-talk Estimation
Estimates the cross-talk/bleed-through of fluorescence between the donor and acceptor’s spectral channels.
F_c = I_{DA} - a (I_{AA} - c I_{DD}) - d (I_{DD} - b I_{AA})
F_c = I_{DA} - a I_{AA} - d I_{DD} \; \text{if} \; b \approx c \approx 0
a = \frac{I_{DA(A)}}{I_{AA(A)}}
b = \frac{I_{DD(A)}}{I_{AA(A)}}
c = \frac{I_{AA(D)}} {I_{DD(D)}}
d = \frac{I_{DA(D)}} {I_{DD(D)}}
b \approx c \approx 0
Parameters:
DD img- $I_{DD}$, donor emission channel image acquired with the donor excitation wavelength.DA img- $I_{DA}$, donor emission channel image acquired with the acceptor excitation wavelength.AD img- $I_{AD}$, acceptor emission channel image acquired with the donor excitation wavelength.AA img- $I_{AA}$, acceptor emission channel image acquired with the acceptor excitation wavelength.mask- labels layer used for masking cellular regions.presented_fluorophore- specifies the fluorophore present in the sample (Afor Acceptor,Dfor Donor).saving_path- directory where the output CSV file with coefficients will be saved.
E-FRET G-factor Estimation
Estimates the G-factor using high and low FRET samples. Supports methods by Zal and Gascoigne, 2004 and Chen et al., 2006.
G = \frac{(I_{DA} - a I_{AA} - d I_{DD}) - (I_{DA}^{post} - a I_{AA}^{post} - d I_{DD}^{post})}{I_{DD}^{post} - I_{DD}} = \frac{F_c - F_{c}^{post}}{I_{DD}^{post} - I_{DD}} = \frac{\Delta F_C}{\Delta I_{DD}}
\Delta F_c = G \cdot \Delta I_{DD}
Parameters:
estimation method- method for G-factor estimation:Zal- linear regression of $\Delta F_c$ vs $\Delta I_{DD}$ (Zal & Gascoigne, 2004).Chen- intersection of lines from high and low FRET samples (Chen et al., 2006).
DD img high FRET/low FRET- $I_{DD}$ images for high and low FRET samples.DA img high FRET/low FRET- $I_{DA}$ images for high and low FRET samples.AA img high FRET/low FRET- $I_{AA}$ images for high and low FRET samples.mask- (forZalmethod) labels layer for ROIs.segment mask- (forZalmethod) if enabled, automatically segments the mask into smaller ROIs.mask high/mask low- (forChenmethod) masks for high and low FRET samples.a&d- pre-calculated cross-talk coefficients.saving_path- directory where the output CSV file with G-factor data will be saved.
E-FRET Estimation
Estimation of the E-FRET with 3-cube approach.
E_{D} = \frac{F_c / G}{F_c / G + I_{DD}}
Parameters:
Сonfig mode- source of FRET coefficients:Default- uses pre-defined coefficients from the plugin directory.Load- allows selecting a custom YAML configuration file viaconfig path.
fret pair- selects the specific fluorophore pair (from the loaded configuration).DD img- donor emission channel image (donor excitation).DA img- acceptor emission channel image (donor excitation).AA img- acceptor emission channel image (acceptor excitation).output type- output image type:Fc- sensitized emission (cross-talk corrected).E_D- donor-centric apparent FRET efficiency (Zal and Gascoigne, 2004).E_A- acceptor-centric FRET ratio (Erickson et al., 2001).Ecorr- FRET efficiency corrected for acceptor photobleaching.
save normalized- if enabled, saves an additional image normalized to the absolute intensity of theAA img.
[!WARNING] Normalized images are intended for visual inspection and mask construction only; they should not be used for quantitative analysis.
| Raw Eapp | 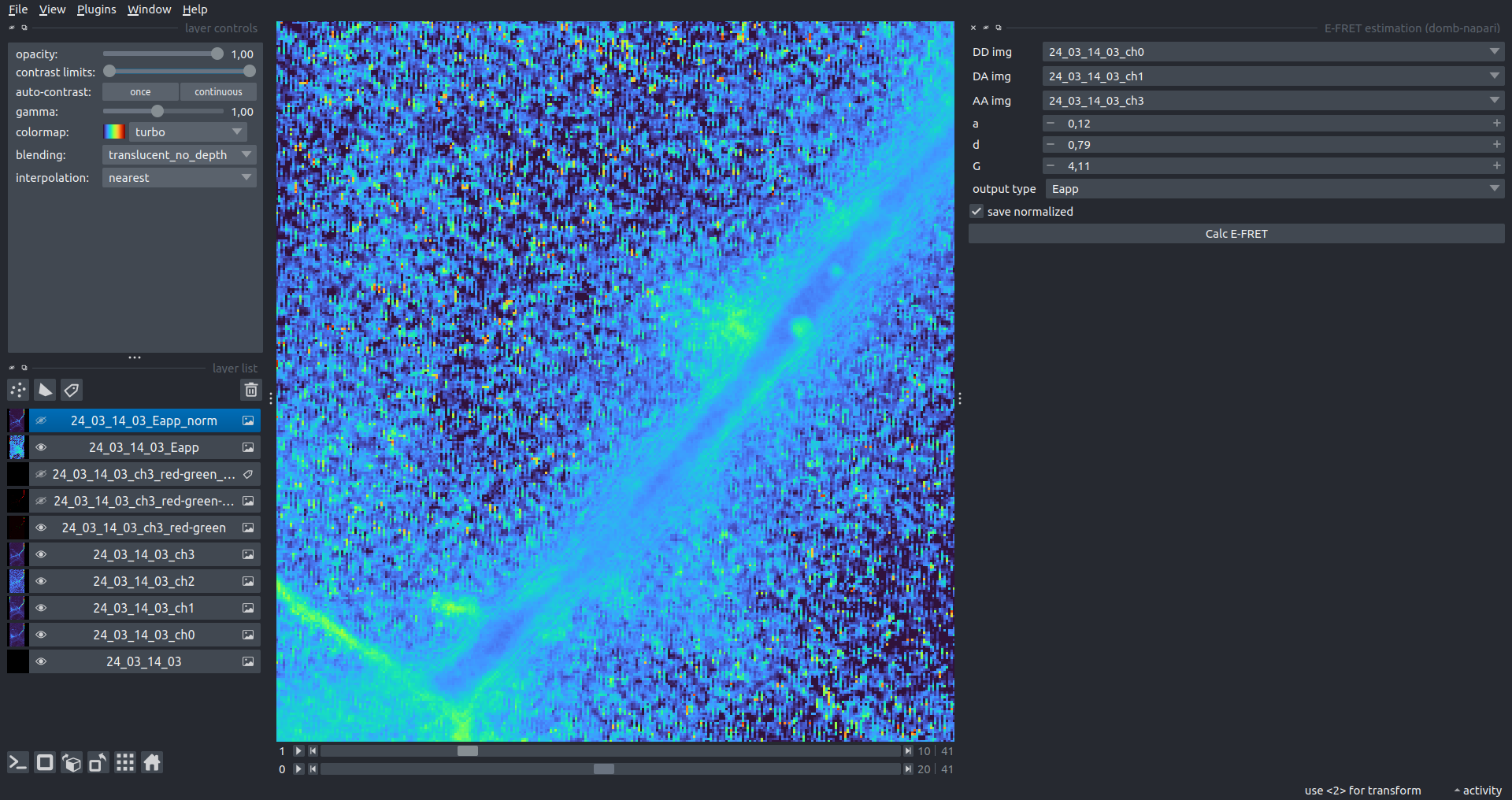 |
|---|---|
| Normalized Eapp | 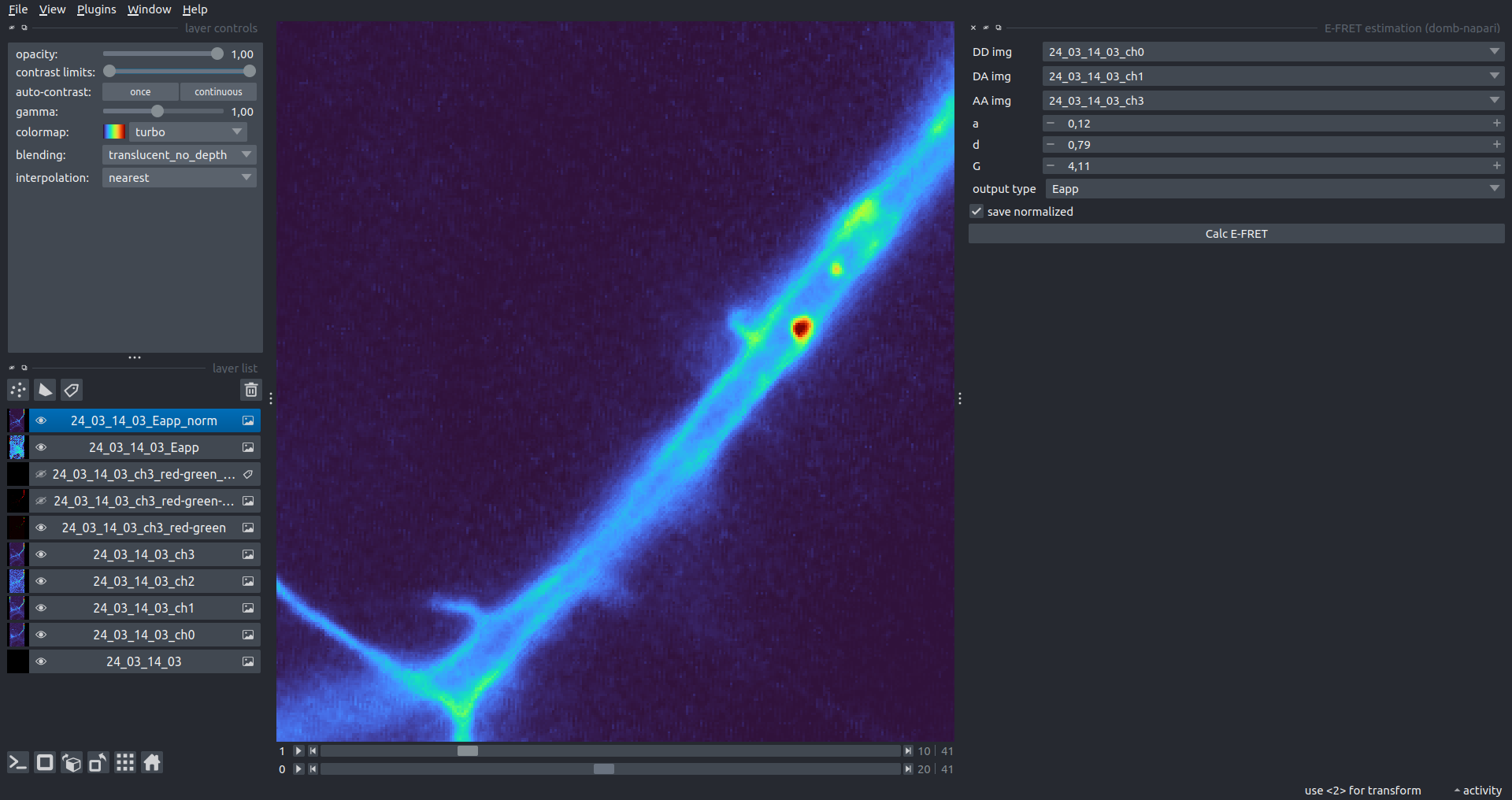 |
FRET Coefficients Configuration
The plugin uses a YAML configuration file to store and load coefficients for different FRET pairs. By default, it uses _e_fret_coefs.yaml located in the plugin directory.
The configuration file structure:
FRET_Pair_Name:
a: 0.031 # Acceptor cross-talk coefficient (I_DA(A) / I_AA(A))
d: 0.415 # Donor cross-talk coefficient (I_DA(D) / I_DD(D))
G: 9.26 # Gauge (G) factor
xi: 0.0535 # Ratio of acceptor/donor extinction coefficients (at donor excitation)
Users can provide a custom configuration file via the E-FRET Estimation widget by switching the Config mode to Load.
Stand-alone E-FRET Module
The core FRET logic is implemented in the stand-alone module _e_fret.py. This module can be used independently of the napari interface for batch processing or custom analysis scripts.
Key classes in _e_fret.py:
CubesFRET- basic class for FRET estimation. Supports calculation of sensitized emission ($F_c$), apparent FRET efficiency ($E_D$), FRET ratio ($E_A$), and corrected FRET efficiency ($E_{corr}$).CrossTalkEstimation- estimates $a$ and $d$ coefficients using linear regression of pixel intensities from single-fluorophore reference samples.GFactorEstimation- estimates the $G$-factor using either the acceptor photobleaching method (Zal and Gascoigne, 2004) or the multi-FRET-level method (Chen et al., 2006).KFactorEstimation- estimates the $k$ factor used for donor/acceptor concentration ratio calculations.
The module utilizes numba JIT compilation for high-performance pixel-wise calculations and pandas/scipy for statistical analysis during calibration steps.
Plotting and Data Frame Saving
ROIs Profiles
This widget builds a plot with mean intensity profiles for each Region of Interest (ROI) in labels. It uses either absolute intensity (if absolute intensity is selected) or relative intensities (ΔF/F0).
Parameters:
time scale- sets the number of seconds between frames for x-axis scaling.values mod- the mode of output profile calculation. Options areΔF/F0(relative intensity changes),ΔF(absolute intensity changes), orabs(absolute intensity value)ΔF win: if theuse_simple_baselineoption is selected, the baseline is the mean of the initial profile points. Otherwise, it defines the median filter window for thepybaselinesestimator.Dietrich std: (forpybaselinesonly) the number of standard deviations for thresholding in the Dietrich method.profiles crop- crops the plotted profiles to the specifiedprofiles range.
| Absolute intensity | 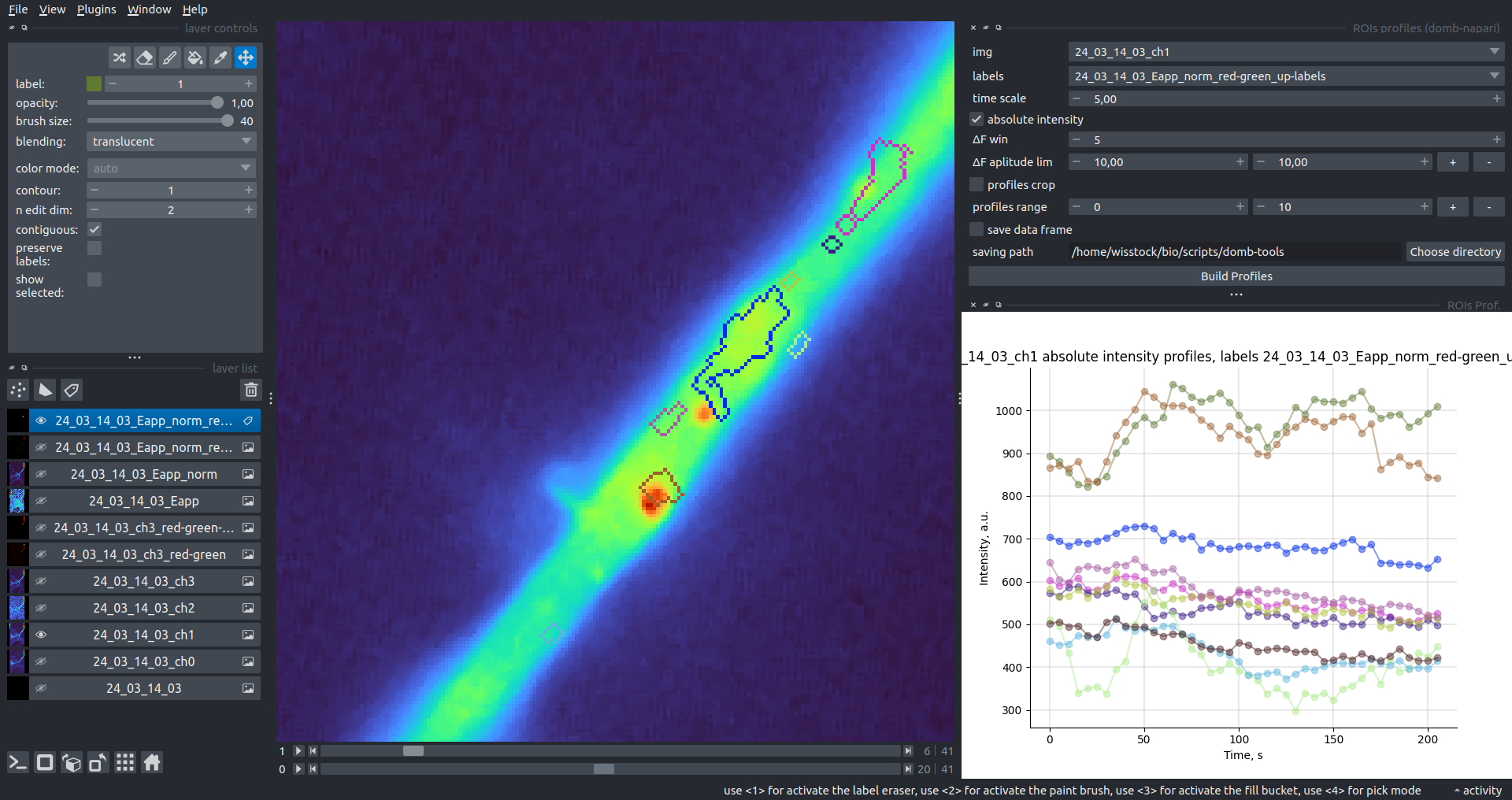 |
|---|---|
| ΔF/F0 | 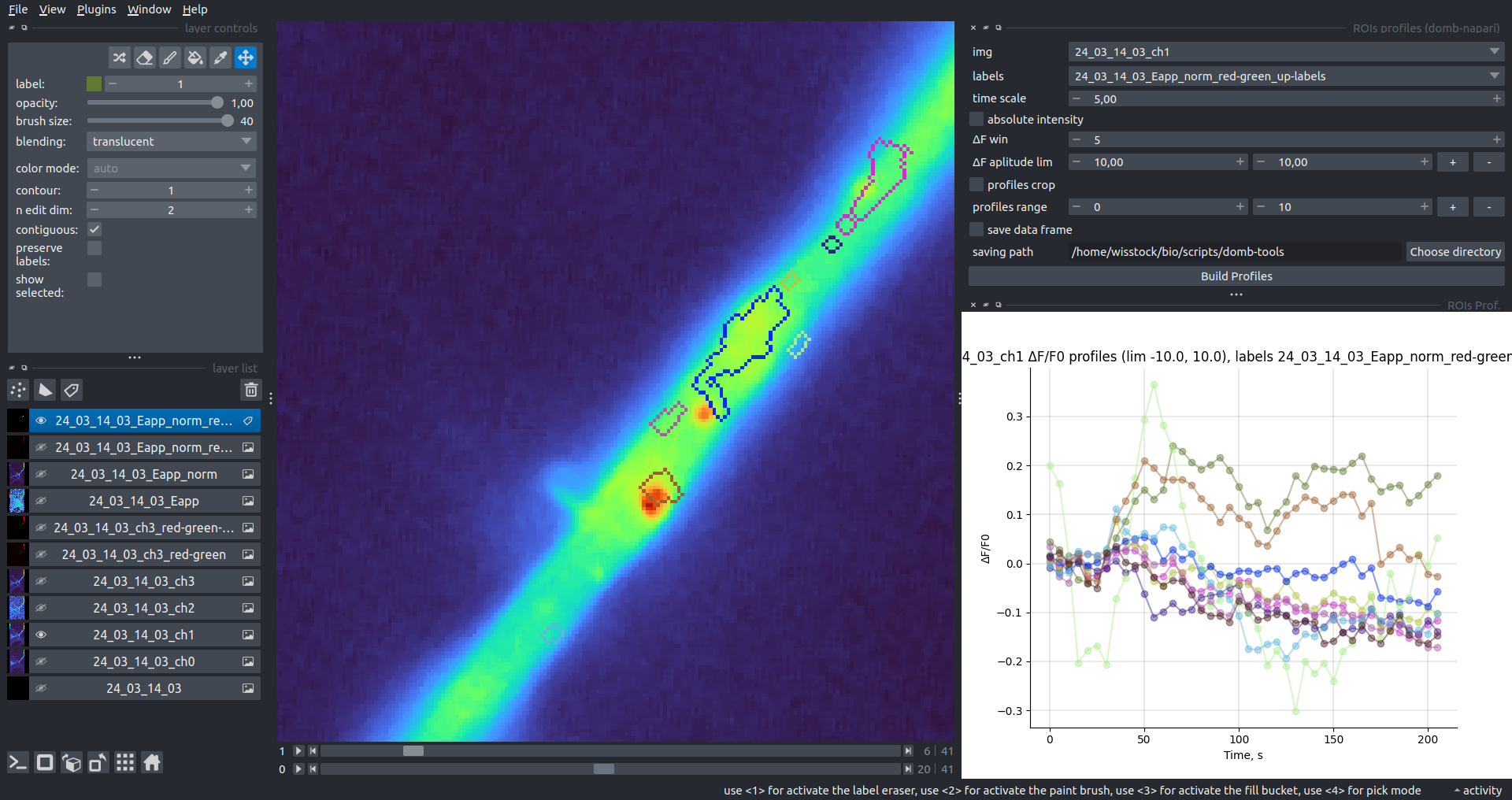 |
Multiple Images Stat Profiles
This widget builds a plot displaying the average intensity of all Regions of Interest (ROIs) specified in lab. It can handle up to three images (img 0, img 1, and img 2) as inputs, depending on the selected profiles num.
time scale, values mod, and ΔF win parameters are identical as described in the ROIs profiles widget.
The stat method allows estimation of intensity and associated errors using the following methods:
se- mean ± standard error of the mean.iqr- median ± interquartile range.ci- mean ± 95% confidence interval (t-distribution).
| Absolute intensity | 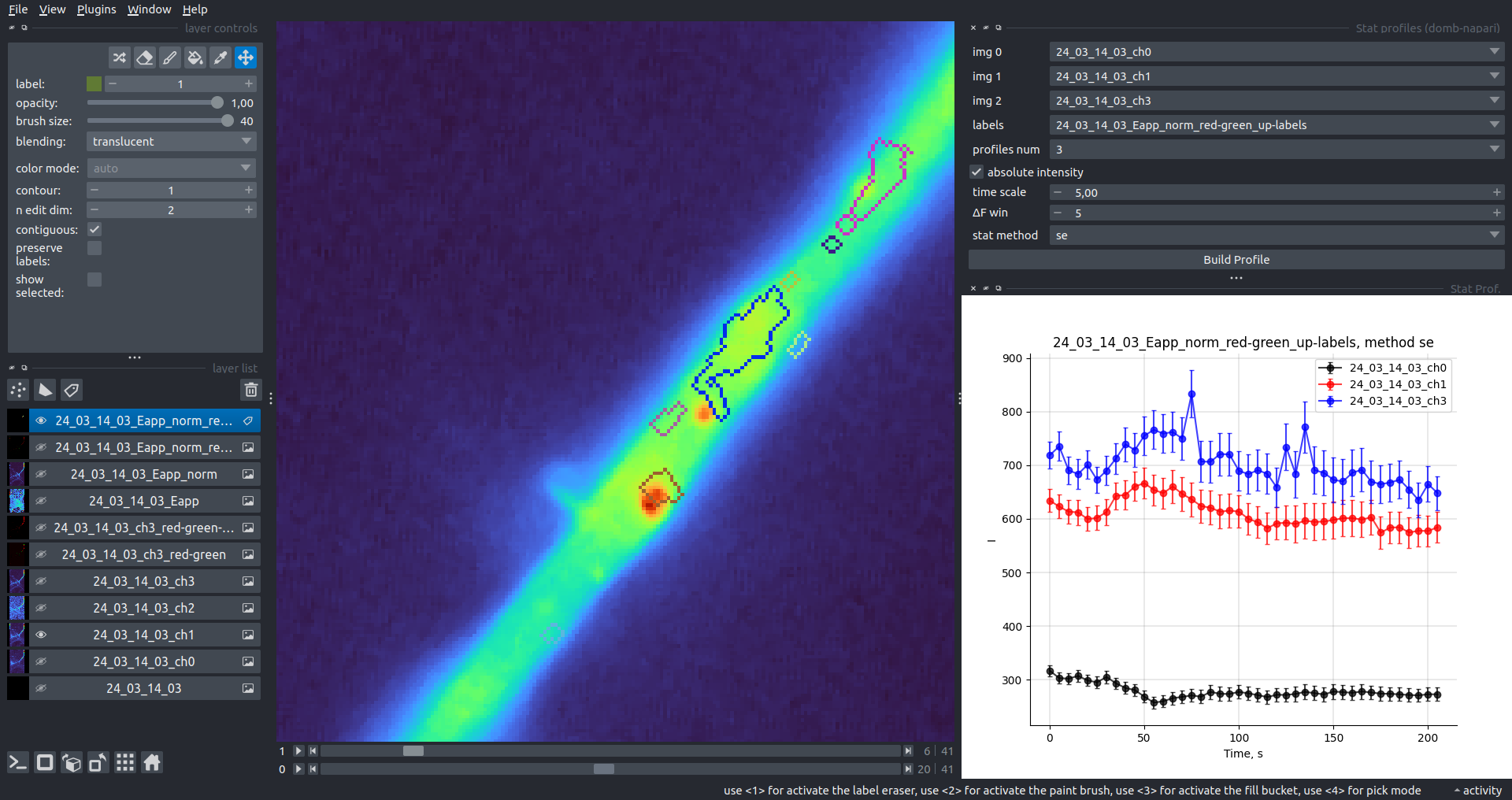 |
|---|---|
| ΔF/F0 | 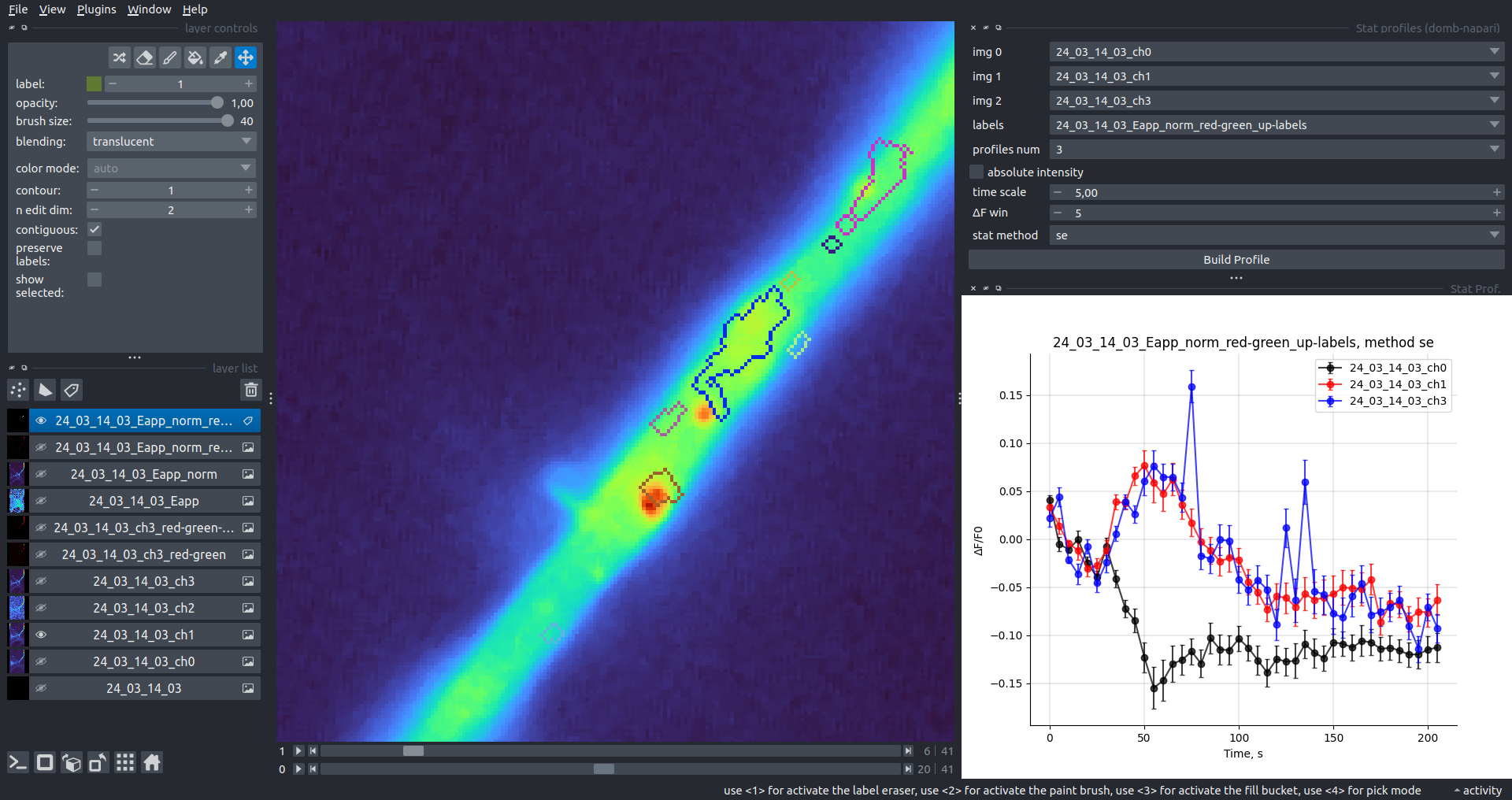 |
Multiple Labels Stat Profiles
This widget builds a plot displaying the averaged intensity of all Regions of Interest (ROI) for one target img. It can handle up to three labels (lab 0, lab 1, and lab 2), depending on the selected profiles num.
time scale, values mod, and ΔF win parameters are identical as described in the ROIs profiles widget.
The stat method allows estimation of intensity and associated errors using the following methods:
se- mean +/- standard error of the mean.iqr- median +/- interquartile range.ci- mean +/- 95% confidence interval based on the t-distribution.
| Absolute intensity | 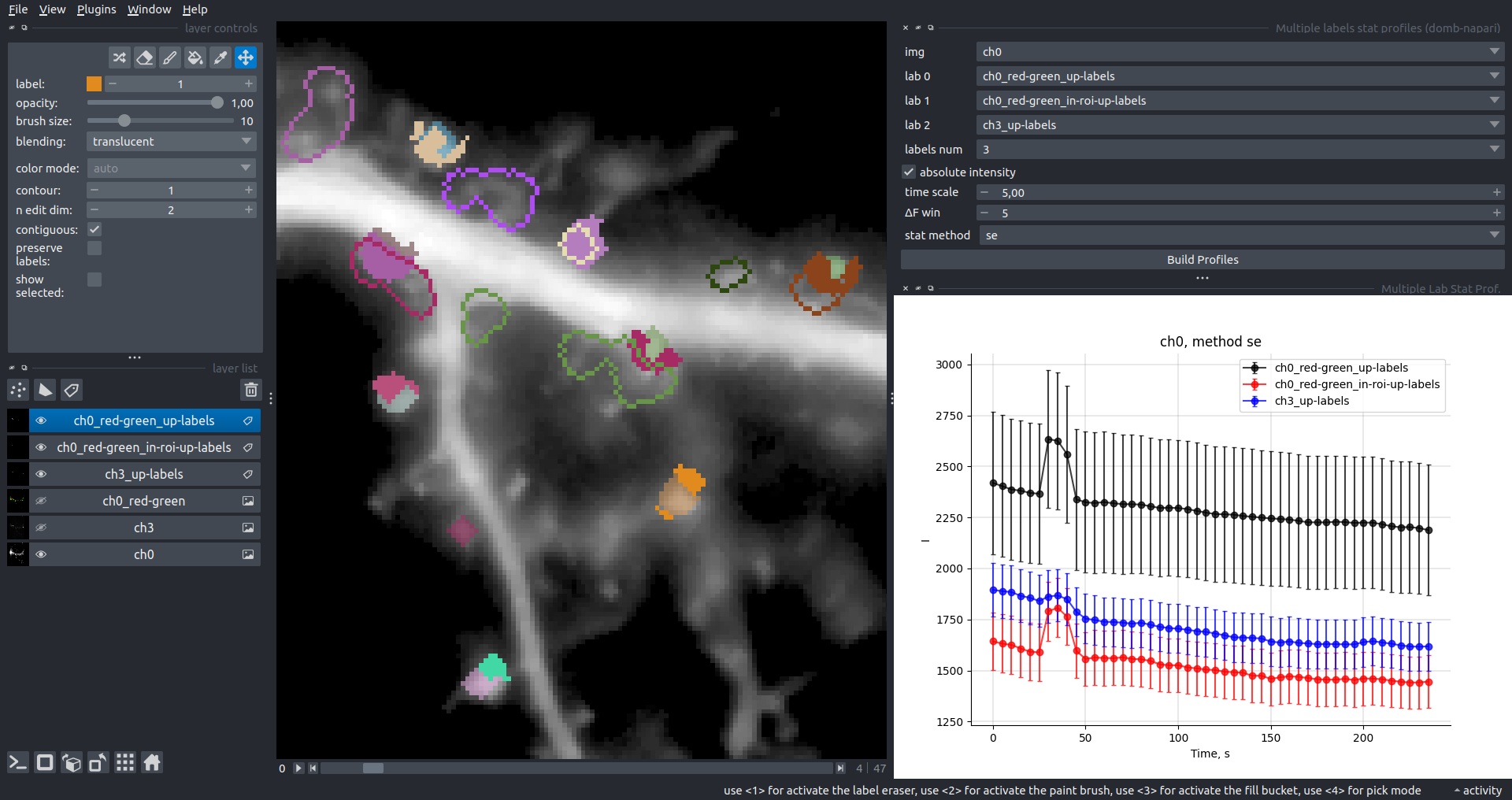 |
|---|---|
| ΔF/F0 | 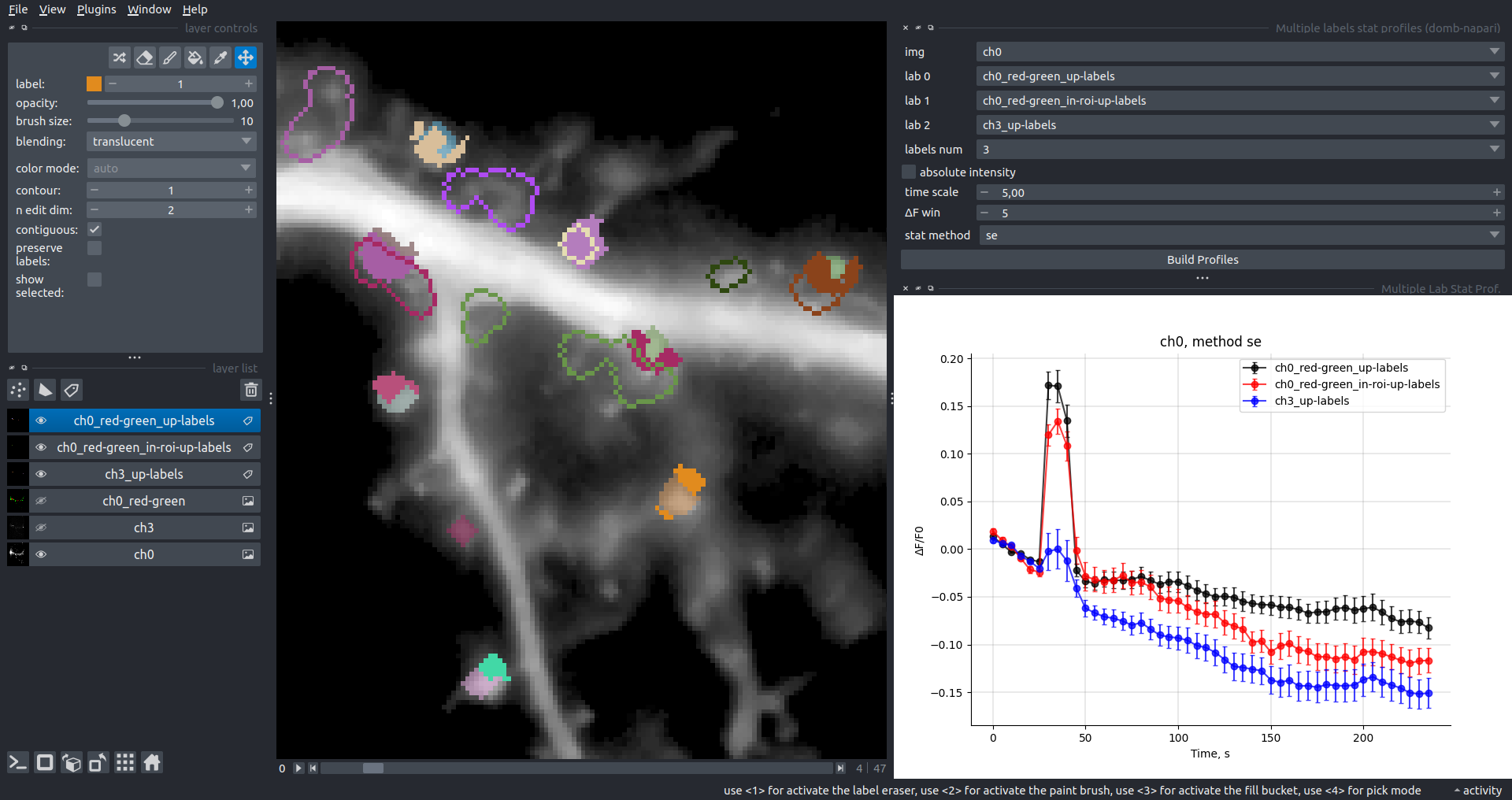 |
Save Data Frame
This widget enables you to save the data frame in CSV format. This is particularly useful for exporting results after examining them with the ROIs Profiles widget.
Parameters:
img- input for a single channel time series image stack.lab- input for a labels layer with ROIs.stim position- input for a points layer with stimulation electrode position, should contain a single point only.time scale- input for frame-to-seconds scaling.ΔF win: baseline window for the simple estimator.Dietrich win&Dietrich std: window size and threshold for thepybaselinesDietrich estimator.save ROIs distances- calculates and saves the average distance (pixels) from ROIs to a stimulation point.custom stim position- uses a point from thestim positionlayer for distance calculations.
The output CSV contains:
id&lab_id: source Image and Labels layer names.roi: ROI index.dist: average distance to stimulation point (if enabled).index&time: frame indices and timestamps.abs_int,dF_int,dF/F0_int: absolute, differential, and relative intensities.base: the baseline estimation method used (simpleordietrich).
How to Cite
If you use this plugin in your work, please cite the following paper:
@article{Olifirov2025,
title = {Local Iontophoretic Application for Pharmacological Induction of Long-Term Synaptic Depression},
volume = {15},
ISSN = {2331-8325},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.21769/BioProtoc.5338},
DOI = {10.21769/bioprotoc.5338},
number = {1373},
journal = {BIO-PROTOCOL},
publisher = {Bio-Protocol, LLC},
author = {Olifirov, Borys and Fedchenko, Oleksandra and Dovgan, Alexandr and Babets, Daria and Krotov, Volodymyr and Cherkas, Volodymyr and Belan, Pavel},
year = {2025}
}
or zenodo:
@misc{https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.14843770,
doi = {10.5281/ZENODO.14843770},
url = {https://zenodo.org/doi/10.5281/zenodo.14843770},
author = {wisstock, },
title = {wisstock/domb-napari: Zenodo release v0.3.0},
publisher = {Zenodo},
year = {2025},
copyright = {MIT License}
}
Version:
- 0.5.2
Last updated:
- 2025-12-23
First released:
- 2024-03-01
License:
- MIT




